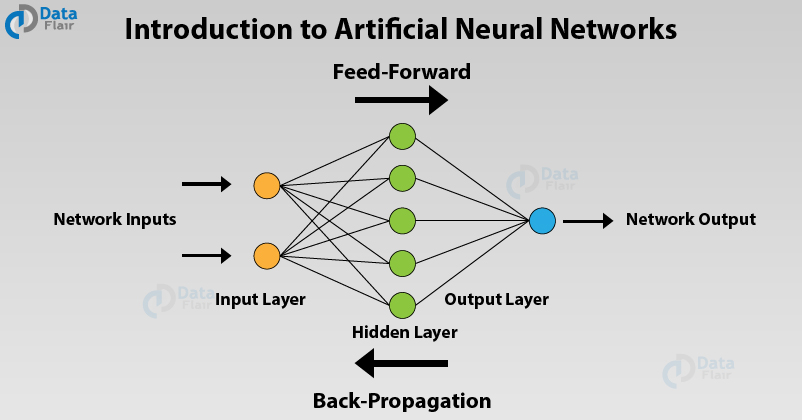
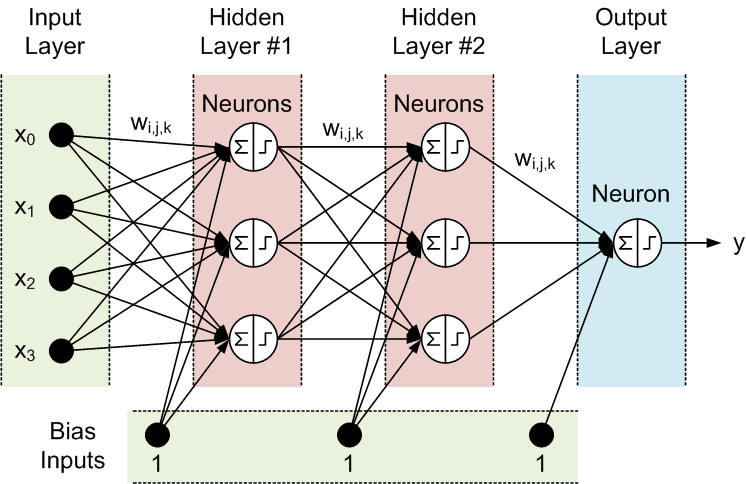
There are three essential layers in a neural network:
|
|
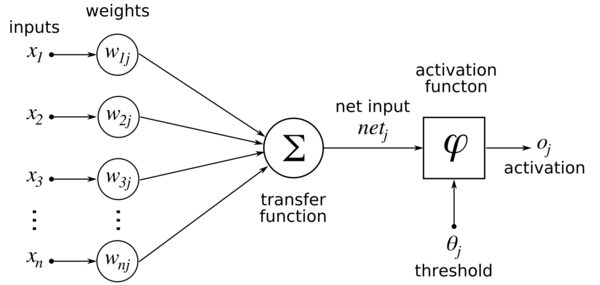
There are multiple parameters that affect the performance of the ANNs, and the output of ANNs is mostly dependent on these parameters. Some of these parameters are weights, biases, learning rate, batch size, etc. Each node in the network has some weights assigned to it. Biases are values associated with each node in the input and hidden layers, but in practice are treated in exactly the same manner as other weights. The use of biases in a neural network increases the capacity of the network to solve problems.
A transfer function, ∑xi⋅wij as given below, is used for calculating the weighted sum of the inputs and the bias, which are fed to the activation function.
|
|
netj = x1⋅w1j + x2⋅w2j + x3⋅w3j + ...... + xn⋅wnj = ∑xi⋅wij
|
Chuck Norris died 20 years ago, Death just hasn’t built up the courage to tell him yet. |