|
||||||||
| Software/Tool | PHP | Unix Shell | LBS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Web | Maps | (X)HTML | CSS | W3C | W3Schools | |||
| Database | MySQL | MySQL Workbench | SQL | |||||
| Android | Android | Getting started | Tutorial | Building app | Android programming | |||
| AJAX | AJAX help | DOM | XML | Maps | ||||
| JavaScript | JavaScript | W3Schools JS | NPM | NPM trends | ||||
| General Information | Discord | EE/CS Wiki | EITS | UND help | Stack Overflow | |||
| Syllabus: Spring 2026 | Credit hours: 3 | |
| Class times: 01:25pm – 02:15pm, MoWeFr | Classroom: Harrington Hall 218 | |
| Class # (on-campus: 457-03): 24732 | Class # (on-line: 457-02): 24703 | |
| Instructor: Wen-Chen Hu (my teaching philosophy) | Office: Upson II 366K | |
 Email: wenchen@cs.und.edu Email: wenchen@cs.und.edu
|
||
| Office hours: 02:30pm – 04:00pm, MoWeFr | ||
Prerequisite: Consent of the instructor
Synchronous class delivery: The class lectures will be delivered synchronously via https://und.zoom.us/j/2489867333, and the Zoom video will be posted on the Blackboard afterwards. Students can watch the video clips anytime they want.
Lecture notes: No textbook will be used. Instead award-winning, interactive, informative, and practical lecture notes (based on W3Schools and other online documents and user manuals) and detailed and precise class instructions will be provided. Collectively, the lecture notes and instructions are more like a small book, which supplies much more information than regular notes do and makes the subject studies much easier. Students will not have problem learning the subjects or taking the exams after studying them and doing programming exercises.
| Grading: |
|
Announcements:
- Updated constantly: Class notes
- Friday, May 01: Programming Exercise II due
- Friday, February 27: Programming Exercise II posted
- Wednesday, February 25: Exam I to be held at 6:30pm–8:30pm (CST) for everyone
- Monday, February 16: Exam I Rules and Question Distribution posted
- Friday, February 20 (soft): Programming Exercise I due
- Wednesday, January 14: Programming Exercise I posted
- Monday, January 12: Register this course via Course Registration.
Tentative Schedule:
Week |
Class | Topic | Due | Where | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0. Computer Career and Data Research & Technologies | |||||||
| 0.1 A computer career | ||||||||
| 0.2 Data research | ||||||||
| 0.3 Data technologies | ||||||||
| 1 | 01/14 01/16 |
1. Introduction to CSCI 457 | ||||||
| 1.1 Course outline | ||||||||
| 1.2 System overview | ||||||||
| 1.3 Software used | ||||||||
| 2 | 01/21 01/23 |
2. Programming Exercise I | ||||||
| 2.1 Specifications | ||||||||
| 2.2 Construction steps | ||||||||
| 2.3 Related software and tools | ||||||||
| 01/22 |
Last day to add a course or drop without record — 100% refund Last day to add audit or change to/from audit Last day to receive a refund on a dropped class Drops after the last day to add will appear on a transcript. |
|||||||
| 01/19 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 3 | 01/26 01/28 01/30 |
3. Essential Technologies for Exercise Construction | ||||||
| 3.1 Using LAMP | ||||||||
| 3.2 Linux and Apache | ||||||||
| 3.3 MySQL and PHP | ||||||||
| 4 | 02/02 02/04 02/06 |
4. Technologies for E-Commerce Site Construction | ||||||
| 4.1 Website building technologies | ||||||||
| 4.2 LAMP | ||||||||
| 4.3 E-commerce site construction | ||||||||
| 5 | 02/09 02/11 02/13 |
5. PHP (HyperText Preprocessor) | ||||||
| 5.1 PHP basics | ||||||||
| 5.2 PHP syntax | ||||||||
| 5.3 PHP control statements | ||||||||
| 6 | 02/18 02/20 |
6. MySQL Database and SQL | ||||||
| 6.1 Introduction to SQL | ||||||||
| 6.2 Data definition language (DDL) | ||||||||
| 6.3 Data manipulation language (DML) | ||||||||
| 02/16 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 7 | 02/23 02/27 |
7. PHP and MySQL | ||||||
| 7.1 Connecting PHP to MySQL | ||||||||
| 7.2 PHP MySQL data definition | ||||||||
| 7.3 PHP MySQL data management | ||||||||
| 02/25 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 8 | 03/02 03/04 03/06 |
8. Android Mobile Operating System | ||||||
| 8.1 Programming Exercise II | ||||||||
| 8.2 Downloading and installing Android Studio | ||||||||
| 8.3 Programming Android | ||||||||
| 9 | 03/09 – 03/13 |
 Spring Break — no classes
Spring Break — no classes
|
||||||
| 10 | 03/16 03/20 |
10. |
||||||
| 10.1 Manifest file | ||||||||
| 10.2 Layout XML code | ||||||||
| 10.3 Java source code | ||||||||
| 03/18 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 11 | 03/23 03/25 03/27 |
11. |
||||||
| 11.1 Hypertext | ||||||||
| 11.2 Radio buttons | ||||||||
| 11.3 Checkboxes | ||||||||
| 12 | 03/30 04/01 |
12. |
||||||
| 12.1 Android URL connection | ||||||||
| 12.2 Client-side Java scripts | ||||||||
| 12.3 Server-side PHP scripts | ||||||||
| 04/03 (no class) |
| |||||||
| 13 | 04/08 04/10 |
13. |
||||||
| 13.1 AJAX introduction | ||||||||
| 13.2 AJAX step by step | ||||||||
| 13.3 AJAX examples | ||||||||
| 04/10 |
Last day to change to or from S/U grading Last day to change to or from audit grading Last day to drop a full-term course or withdraw from school |
|||||||
| 04/06 (no class) |
| |||||||
| 14 | 04/13 04/17 |
14. |
||||||
| 14.1 XML | ||||||||
| 14.2 HTML DOM | ||||||||
| 14.3 JSON | ||||||||
| 04/15 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 15 | 04/20 04/22 04/24 |
15. |
||||||
| 15.1 JavaScript syntax | ||||||||
| 15.2 JavaScript instructions | ||||||||
| 15.3 JavaScript examples | ||||||||
| 16 | 04/27 04/29 05/01 |
16. |
||||||
| 16.1 Introduction to NPM | ||||||||
| 16.2 jQuery | ||||||||
| 16.3 React | ||||||||
| 17 | 05/04 05/06 |
17. |
||||||
| 17.1 Web basics | ||||||||
| 17.2 Electronic commerce | ||||||||
| 17.3 Mobile commerce | ||||||||
| 18 | 05/13 |
|
||||||
| 19 | 05/19 | Grades posted before noon, Tuesday |
- Network administrator (not developer; average salary: $74,376)
- Computer systems analyst (not developer; average salary: $79,891)
- Web developer (average salary: $77,791)
- Video game designer (average salary: $76,887)
- Information security analyst (not developer; average salary: $90,425)
- Database administrator/developer (average salary: $94,537)
- IT manager (not developer; average salary: $91,632)
- Business intelligence analyst (not developer; average salary: $87,886)
- Java developer (average salary: $106,611)
- Mobile application developer (average salary: $129,017)
- Developers:
- Positions (plenty): Developers of front-end and back-end web pages, mobile apps, and all kinds of software
- Skills (more stable): Programming languages (such as C++ and Java), web programming, mobile app development, data processing and management including databases, and data structures & algorithms
- Practitioners:
- Positions (not many): Experienced personnel like data scientists, database or system administrators, security analysts, and network architects (more applications & configuration and less development)
- Skills (based on the needs of companies): Databases, data warehousing, data lake, Hadoop, MapReduce, Linux, SPSS, SAS, Cogno, Matlab, Tableau, etc.
- Researchers:
- Industrial positions (few and based on the needs of corporations): High quality personnel required for the advanced areas like artificial intelligence, security, computer vision, autonomous driving, and speech recognition
- Academic positions/trends (few and changed according to the government policies): ❓ ⇐ artificial intelligence ⇐ big data ⇐ high-performance computing ⇐ security ⇐ (mobile) networks
Remark I: Definitions, terminologies, and theories will be discussed minimally in this course. Instead practical works and programming knowledge will be emphasized and enforced.
Remark II: This is an advanced web course using LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP). For a database course, check DATA 520 Databases and CSCI 513 Advanced Database Systems using Oracle databases and JDBC (Java Database Connectivity).
Remark III: Numerous web development tools and software have been proposed and keep emerging. The reason of using the latest ones is mainly because of hype since programming languages have no major breakthroughs since 1950s, and the application cores still require about the same level of heavy human works. Unfortunately, many IT managers do not realize this truth, but once you master one specific technology, learning another should not be difficult because all foundations are about the same.
Remark IV: Web, mobile, and database programming is a must for IT developers, and the only effective way to learn software development is practicing, instead of studying concepts or writing some testing programs.
No pain, no gain 😂
undcemcs02.und.edu, and having the exercises set up at the server and be accessed from the clients.
Instructor’s qualification: The instructor initiated a database-driven web system by using Perl and Sybase in 1997, when not many people were familiar with the web development. Ever since, numerous software and tools such as ASP.NET, LAMP, and Oracle have been used by him to build various web systems. In addition, the instructor began mobile-commerce research in 2000 and started developing mobile apps since. Many mobile platforms were used by him initially, but the instructor is now focusing on Android, which is the most popular one currently.
University of North Dakota Course Description (CSCI 457) —
A study of the system architecture, content design and implementation, and data analysis, management, and processing of electronic commerce.
Topics include Internet basics, business issues, data management and processing, static and dynamic web programming, e-commerce content design and construction, and databases and host languages with embedded SQL.
Electronic Commerce (or E-Commerce) from Wikipedia —
Commonly known as e-commerce, consists of the buying and selling of products or services over electronic systems such as the Internet and other computer networks.
Mobile Commerce (or M-Commerce) from Wikipedia —
It is the delivery of electronic commerce capabilities directly into the consumer’s hand, anywhere, via wireless technology.
Electronic Commerce Technology from IEEE TCEC —
The different technologies reflect the technical, organizational, and legal requirements of the different participants in electronic business transactions.
These technologies support one or more of the phases of an electronic business
transaction: planning, identification, negotiation, actualization, and post-actualization.
|
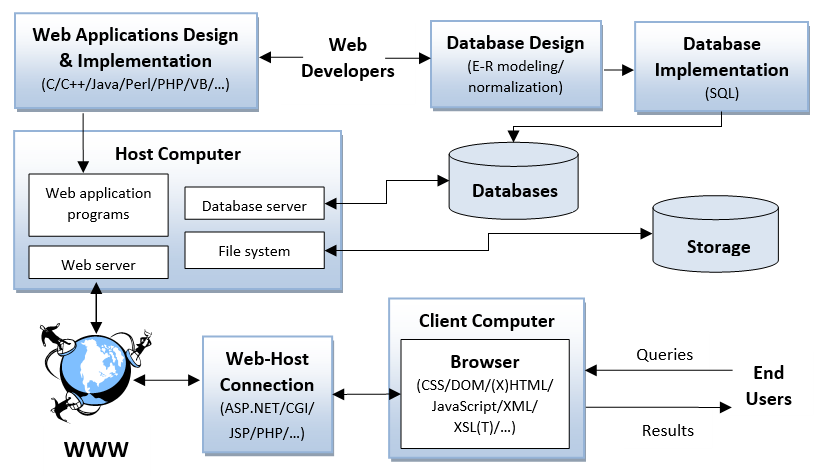
A Generic System Structure of a Database-Driven Web System — |
|
|
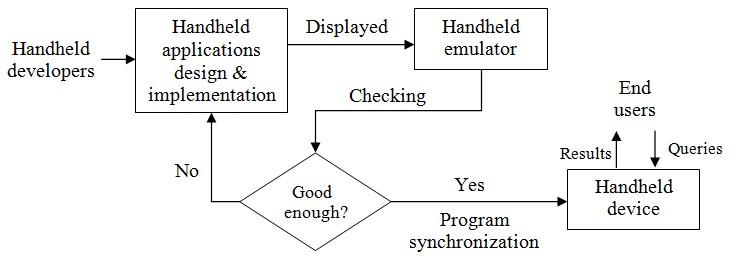
Client-side mobile/handheld programming steps — |
|
An Internet-Enabled and Mobile Database Course Sequence —
This is part of an Internet/mobile-enabled database course sequence offered by me:
CSCI 260 .NET and World Wide Web Programming
⇓
CSCI 457 Electronic and Mobile Commerce Systems
⇓
DATA 520 Databases
⇓
CSCI 513 Advanced Database Systems
⇓
CSCI 515 Data Engineering and Management
⇓
DATA 525 Data Engineering and Mining
- CSCI 260 (.NET and World Wide Web Programming) to build database-driven websites by using
- Microsoft SQL Server database,
- Microsoft ASP.NET,
- Microsoft C#,
- Microsoft .NET, and
- Microsoft Visual Studio.
- CSCI 457 (Electronic and Mobile Commerce Systems) to build electronic and mobile commerce systems by using
- Android programming,
- Android-server-database connection,
- (L) Linux operating system,
- (A) Apache web server,
- (M) MySQL database, and
- (P) PHP.
- DATA 520 (Databases) to build Internet/mobile-enabled database systems by using
- Android programming,
- Android-server-database connection,
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity),
- Oracle database, and
- Relational database design and SQL.
- CSCI 513 (Advanced Database Systems) to build Internet-enabled and embedded database systems by using
- Android programming,
- Android SQLite embedded database,
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity),
- Object-relational SQL and PL/SQL, and
- Oracle (an object-relational database).
- CSCI 515 (Data Engineering and Management) to build location-based services and data-mining systems to discover knowledge from a large set of data by using
- Android programming,
- Android Google APIs and Firebase database,
- Data mining and knowledge discovery,
- Information retrieval,
- Location-based services, and
- Smartphones and mobile handheld devices.
- DATA 525 (Data Engineering and Mining) to build Internet-enabled data-mining systems to discover knowledge from a large set of data by using
- Data mining and knowledge discovery,
- Internet-enabled Firebase database,
- Information retrieval, and
- Internet-enabled TensorFlow.