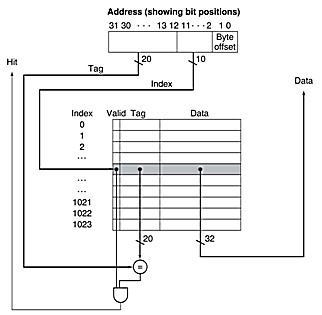
The block size of the previous cache was one word, but normally it is several. Assume a direct-mapped cache has the following features (note that the following figure is only one of the caches described):
|
|
The size of the
tag field is therefore
32 - ( n + m + 2 )The total number of bits in a direct-mapped cache is
2n × ( block size + tag size + valid field size )Since the block size is 2m words (2m+5 bits), and we need 1 bit for the valid field, the number of bits in such a cache is
2n×(2m×32+(32-n-m-2)+1) = 2n×(2m×32+31-n-m)