if Statement
| A nested if is an if statement that is the target of another if or else. Nested if statement means an if statement is inside another if statement. Yes, Java allows us to nest if statements within if statements; i.e., we can place an if statement inside another if statement. |
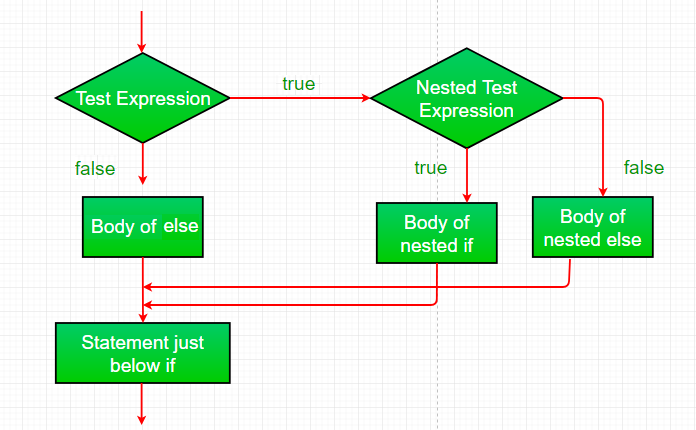
|
|
|
I came up with a new word yesterday: Plagiarism. |


