- Start Running the Android Database Application. In order to access the SQLite database from the command line shell, the application has to be active.
- Activate a Command Prompt. Pick the following Windows options:
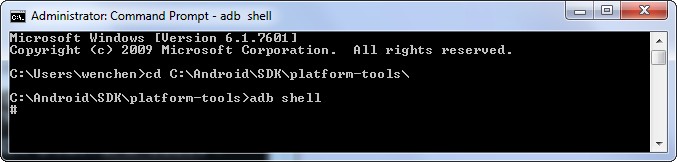
- Enter the Directory platform-tools. For my computer, the directory is located at
- Start a Remote Shell. Enter the command “
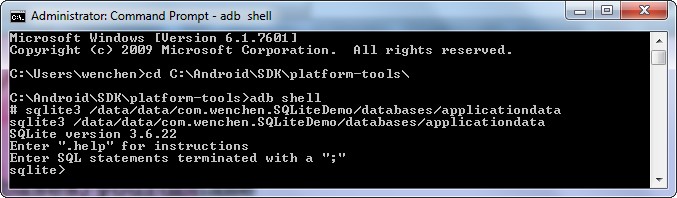
- Enter the Database. Enter the command:
yourpackage: My package is namedcom.example.wenchen.sqlitedemoandyourdbname: My database is namedapplicationdata.- Start Managing the Database. Check the Command Line Shell for SQLite.
- Exit the Database and adb. Enter the commands:
Start ⇒ All Programs ⇒ Accessories ⇒ Command Prompt
C:\> cd C:\Android\SDK\platform-tools\To find where your Android SDK is located, pick the following Android Studio options:
Tools ⇒ SDK ManagerThe location can be found on the top of the screen.
adb shell” where adb is Android Debug Bridge, a versatile command line tool that lets you communicate with an emulator instance or connected Android-powered device.
# sqlite3 /data/data/yourpackage/databases/yourdbnameFor my computer, the command is as follows:
# sqlite3 /data/data/com.example.wenchen.sqlitedemo/databases/applicationdata;where
†If you encounter a problem of
Error: unable to open database "applicationdata": unable to open database filecheck the Stackoverflow to solve it by adding two commands:
shell> adb root shell> adb root restarting adbd as root shell> adb shell
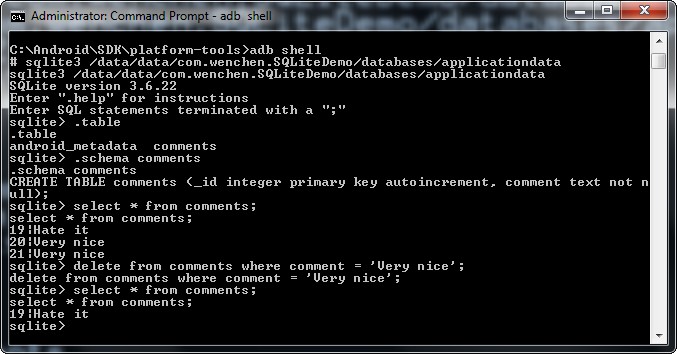
sqlite> .exit .exit # exit exit C:\Android\SDK\platform-tools>