Using Firebase Database (Android)
The Firebase database is a NoSQL, real-time, and cloud-hosted database.
Data is stored as JSON and synchronized in real-time to every connected client.
The following steps show how to use the Firebase database:
†For the Web, check Using Firebase Database (Web).
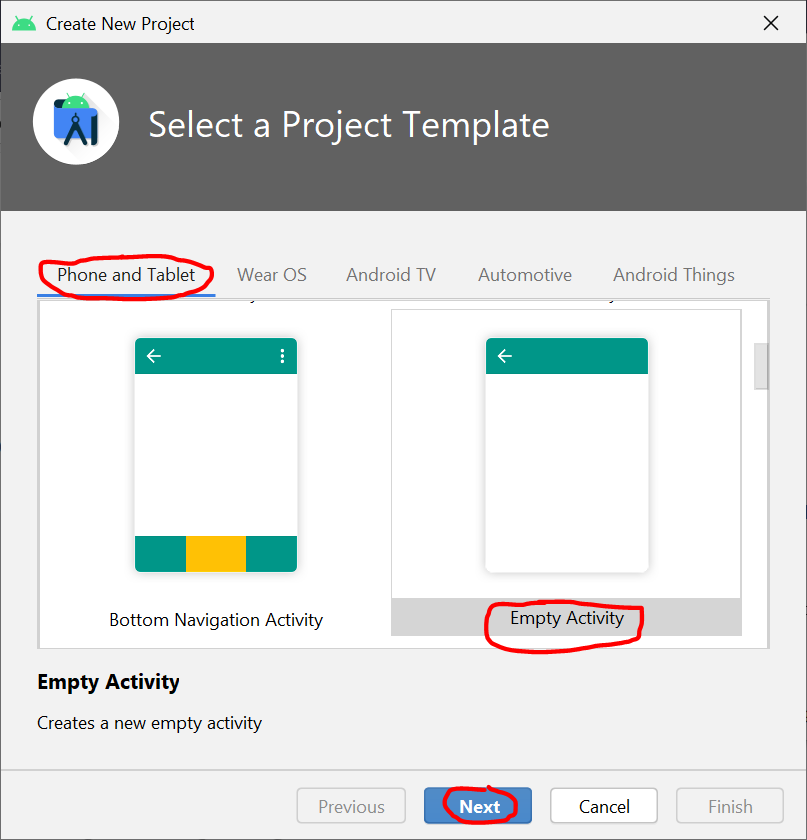
- Open Android Studio and create a new project or open an existing project.
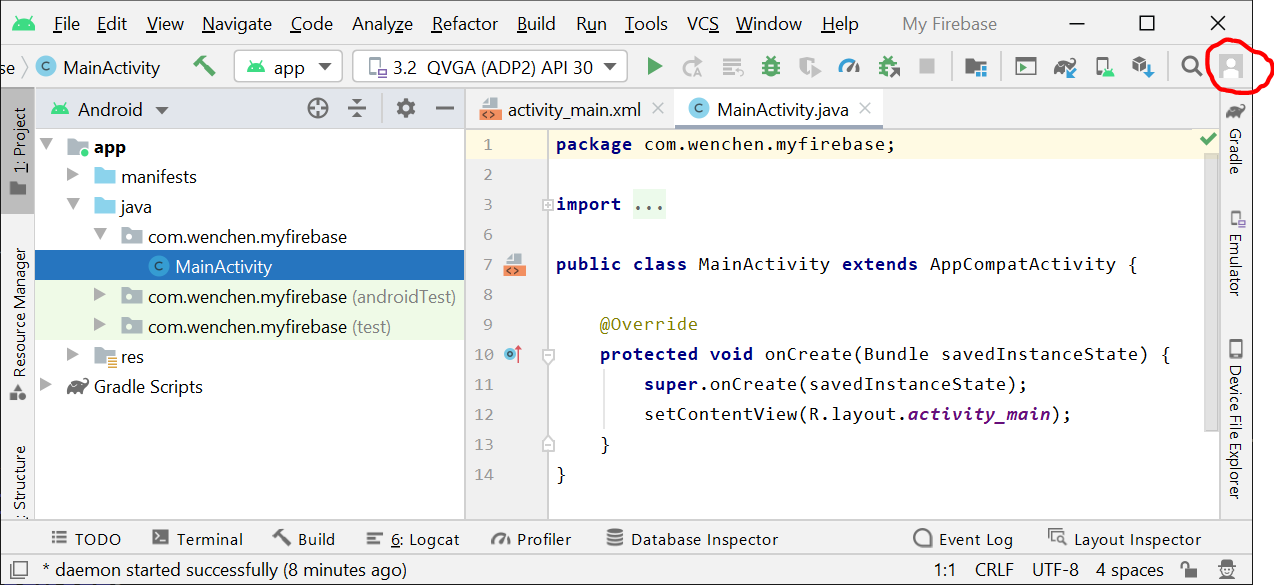
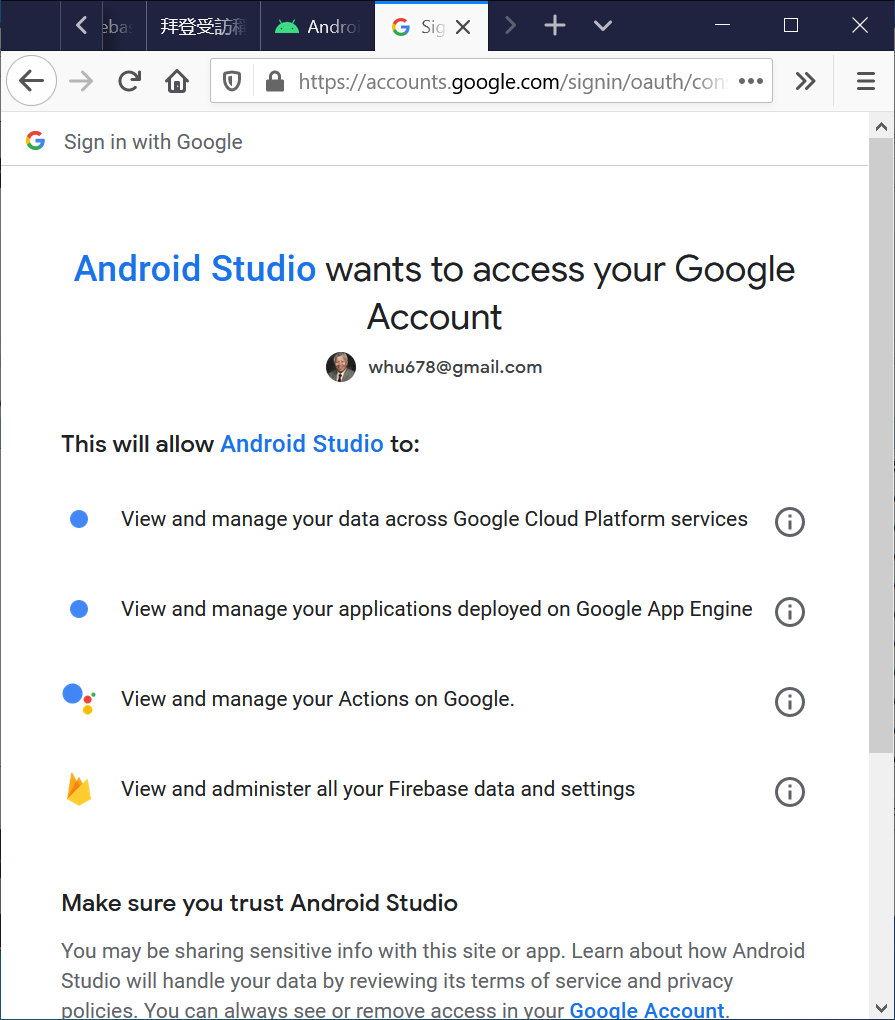
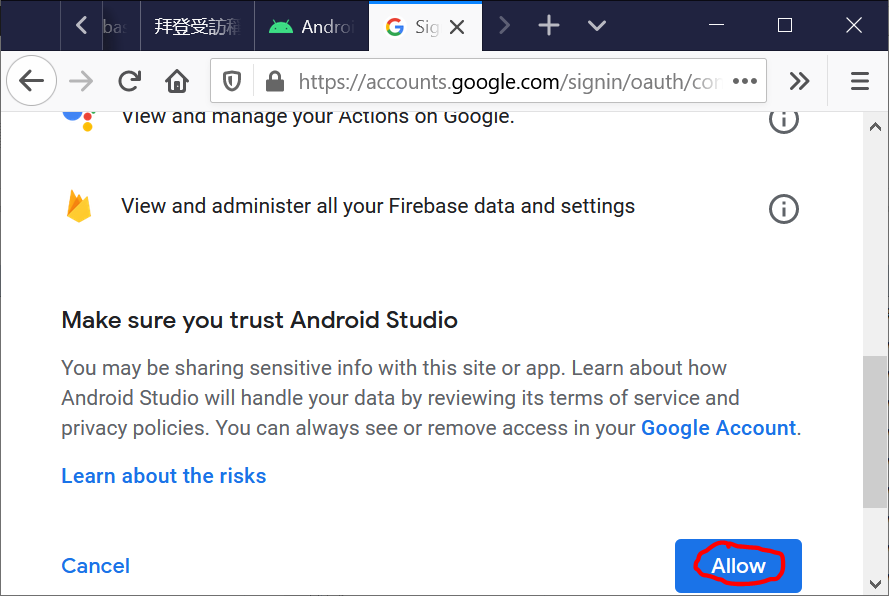
- In Android Studio, log in with your email address.
You can find the login button at the top right corner of the Android Studio.
(Remember the email address that you use here.)
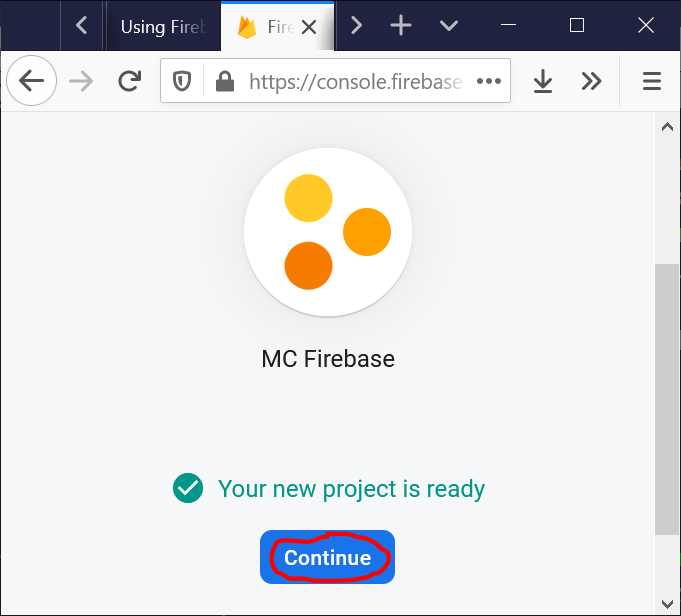
- Go to Google Firebase console and make an account to gain access to their console.
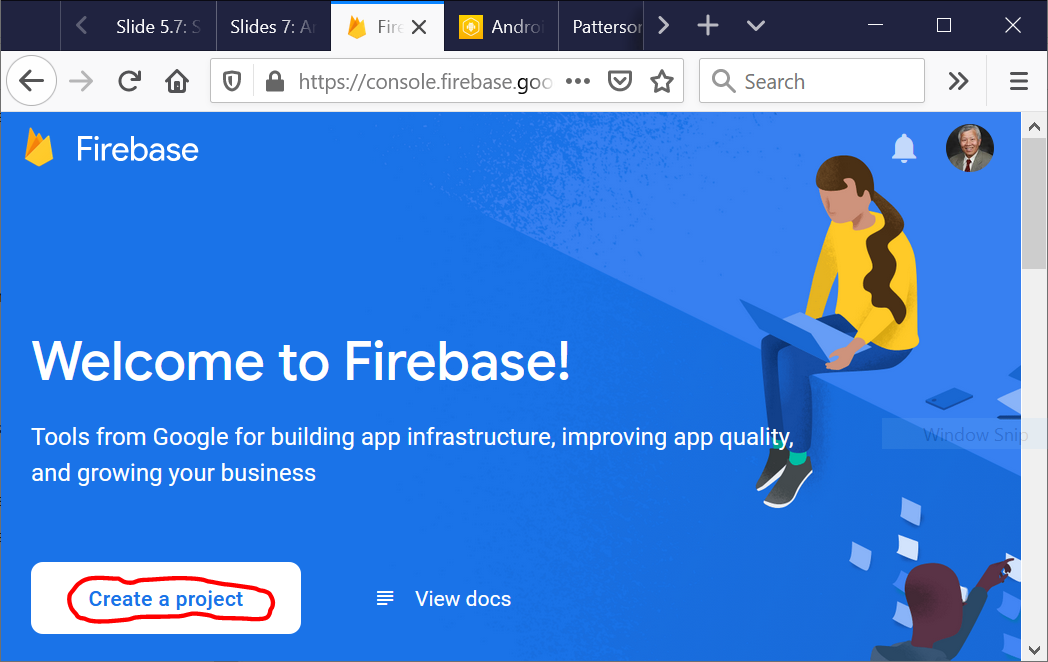
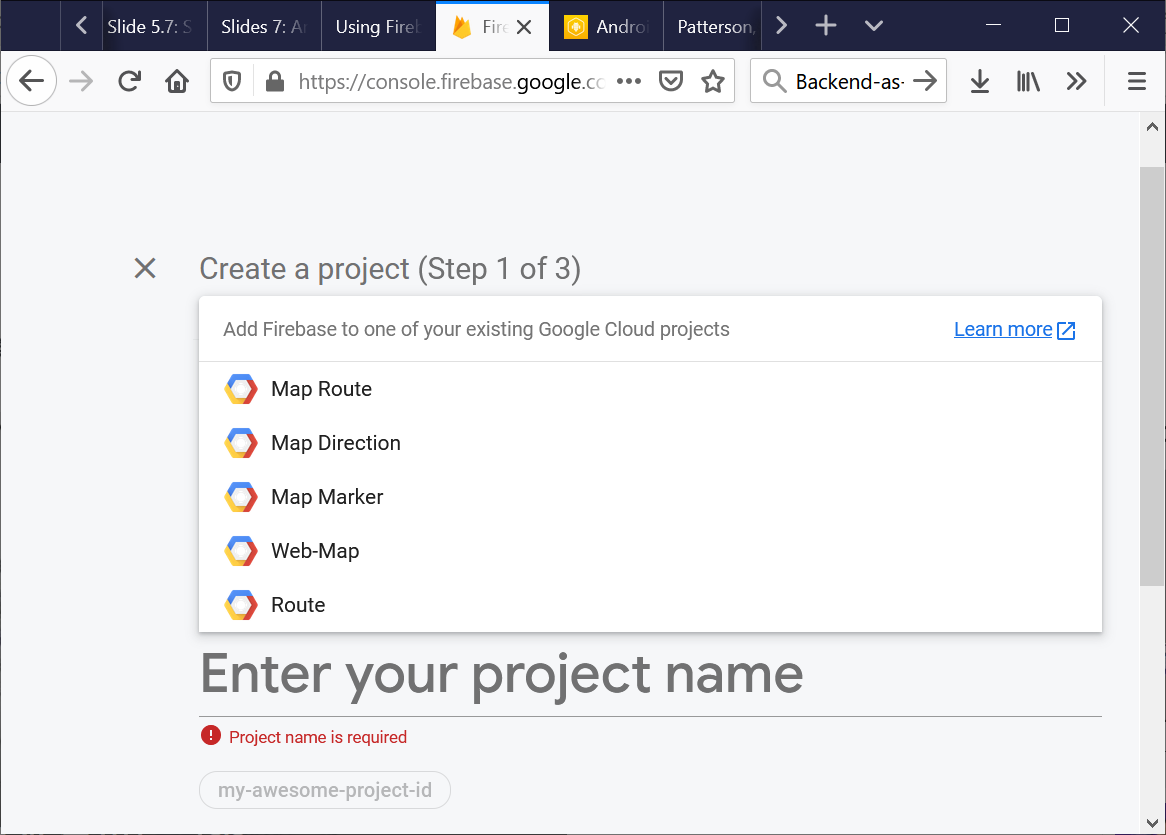
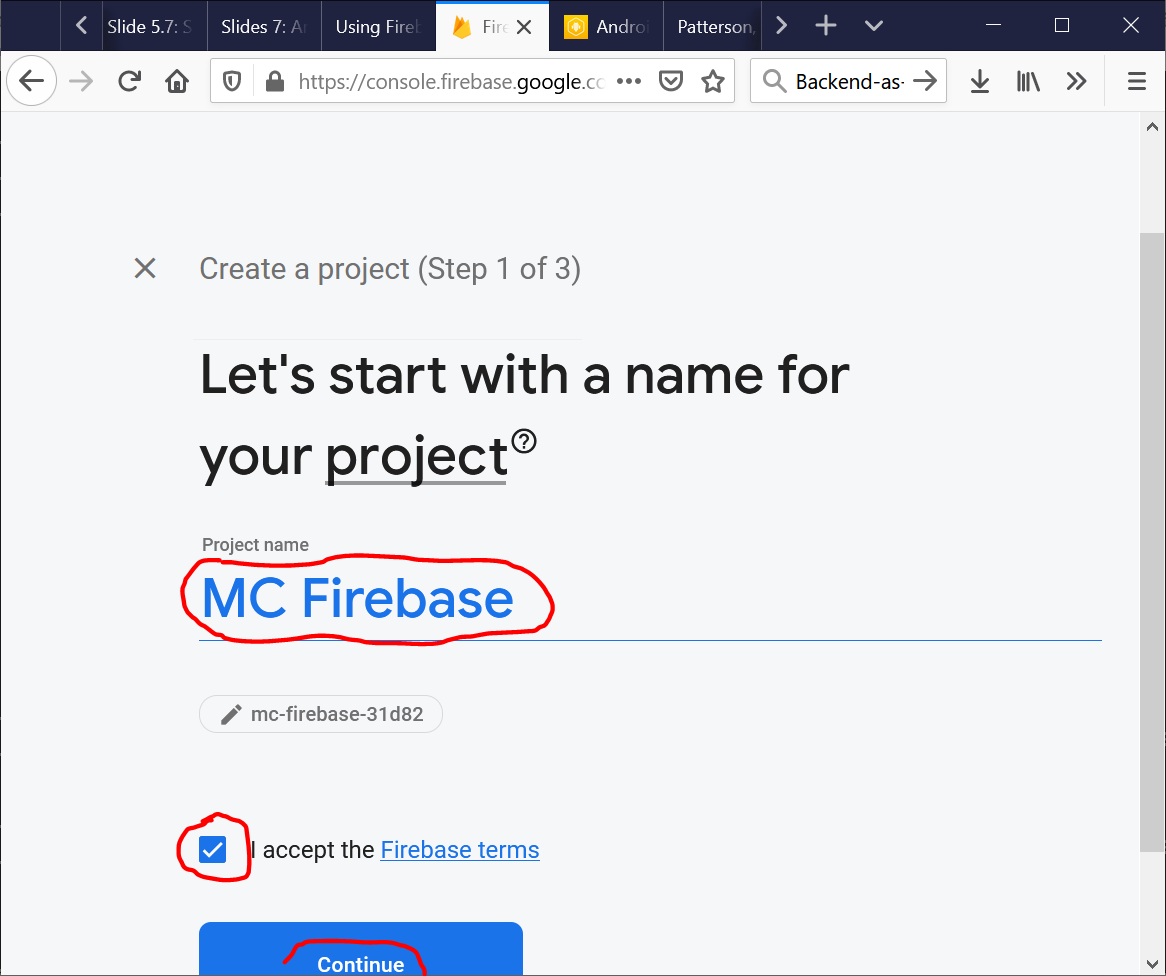
- Start creating your first Firebase project:
Select the “Test Mode.”
Otherwise, your code has to include authentication.
⇒ |

|
- Now, come back to your Android Studio project.
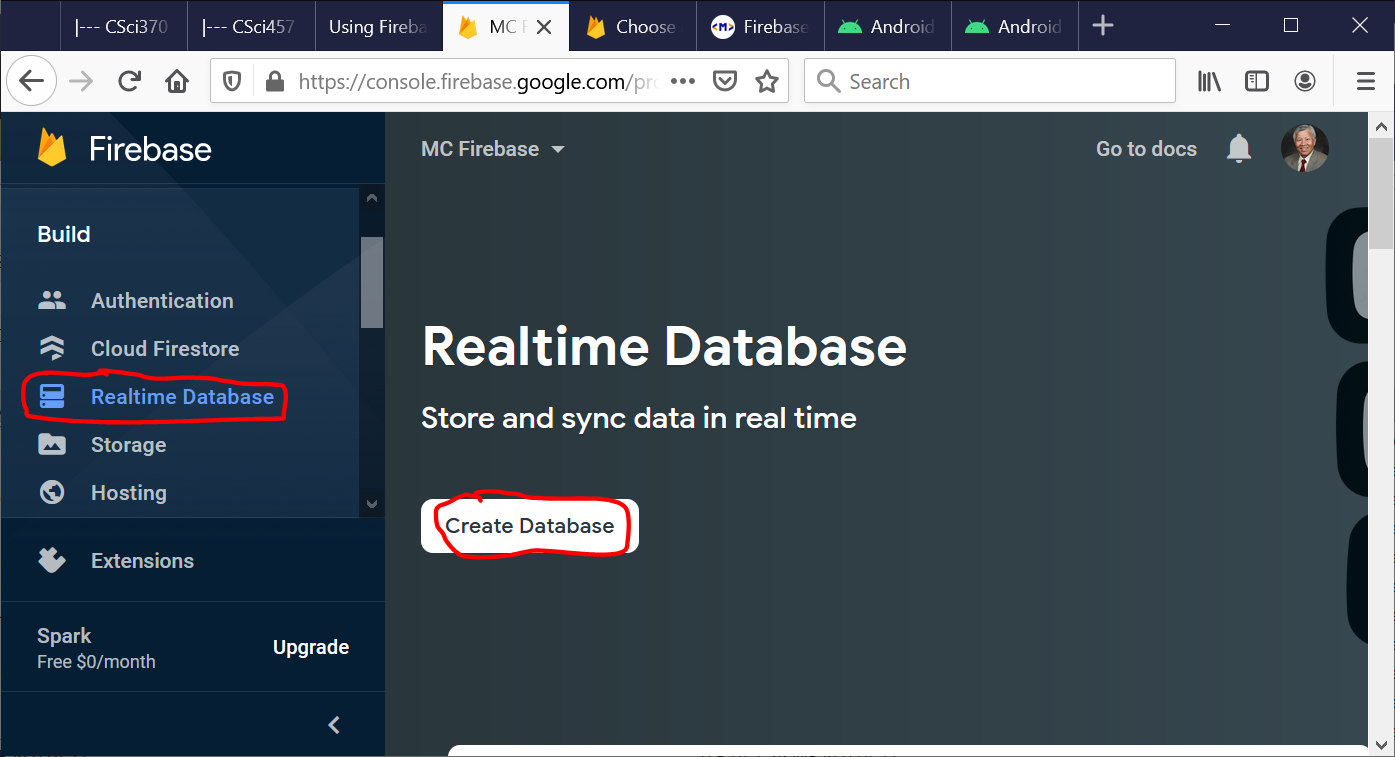
Connect the Android Studio project to the Firebase project by clicking on Tools ⇒ Firebase ⇒ Realtime Database ⇒ Save and retrieve data.

- After that click on “Connect to Firebase,”
a list of projects will be shown to you.
Select the project that you have created on the Firebase website and click on “Connect to Firebase.”
- Next, you have to add the dependency of Firebase Database in your project by clicking on “Add the Realtime Database to your app” button and then “Accept Changes.”
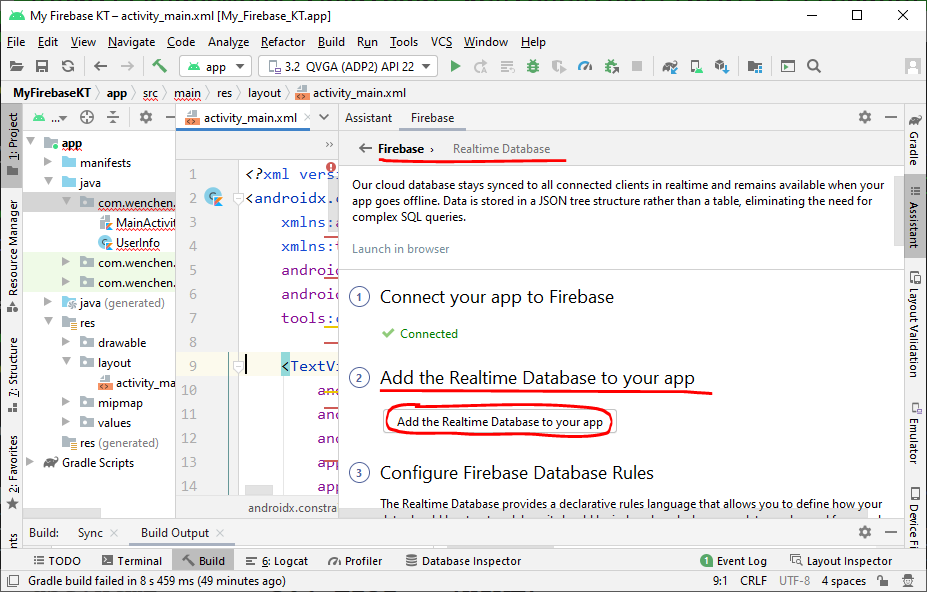
⇓ (after checking “Add the Realtime Database to your app”)

The build.gradle (Module: My_Firebase.app) file before adding the dependencies is
|
MyFirebase\build.gradle (Module: My_Firebase.app)
|
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
}
android {
compileSdkVersion 30
buildToolsVersion "30.0.2"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.wenchen.myfirebase"
minSdkVersion 16
targetSdkVersion 30
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'),
'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.2.0'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.3.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.0.4'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.2'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.3.0'
}
|
⇓ (after adding the dependencies)
|
MyFirebase\build.gradle (Module: My_Firebase.app)
|
plugins {
id 'com.android.application'
id 'com.google.gms.google-services'
}
android {
compileSdkVersion 30
buildToolsVersion "30.0.2"
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.wenchen.myfirebase"
minSdkVersion 16
targetSdkVersion 30
versionCode 1
versionName "1.0"
testInstrumentationRunner "androidx.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android-optimize.txt'),
'proguard-rules.pro'
}
}
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.2.0'
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.3.0'
implementation 'androidx.constraintlayout:constraintlayout:2.0.4'
implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-database:19.6.0'
testImplementation 'junit:junit:4.+'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.ext:junit:1.1.2'
androidTestImplementation 'androidx.test.espresso:espresso-core:3.3.0'
}
|
If there is an error of
File google-services.json is missing from module root folder. The Google Services Plugin cannot function without it.”
Take the following actions:
-
Go to Firebase Console .
-
Select your project.
-
Go to “settings ⇒ project settings.”
-
Download and add the
google-services.json file to the app folder of your app at
MyFirebase\app\google-services.json
The rest of the code is given as follows:
The
AndroidManifest.xml file does not need to be changed as follows:
|
MyFirebase\app\manifests\AndroidManifest.xml
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.wenchen.myfirebase">
<application
android:allowBackup = "true"
android:icon = "@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label = "@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon = "@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl = "true"
android:theme = "@style/Theme.MyFirebase">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name = "android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name = "android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
|
Add code to the
main_activity.xml file.
This application updates and shows the user’s profile consisting of a name and an email address.
So, we will have one
TextView for showing the profile and two
EditTexts for getting the new values from the user, and an update button.
The code for the
main_activity.xml file is given as follows:
|
MyFirebase\app\res\layout\activity_main.xml
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools = "http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id = "@+id/activity_main"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "match_parent"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:paddingBottom = "@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft = "@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight = "@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop = "@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context = "com.wenchen.myfirebase.MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id = "@+id/txt_user"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:paddingBottom = "@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop = "@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:textSize = "20dp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:orientation = "vertical">
<com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content">
<EditText
android:id = "@+id/name"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:hint = "@string/name"
android:inputType = "textCapWords"
android:maxLines = "1" />
</com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout>
<com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content">
<EditText
android:id = "@+id/email"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:hint = "@string/email"
android:inputType = "textEmailAddress"
android:maxLines = "1" />
</com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout>
<Button
android:id = "@+id/btn_save"
style = "?android:textAppearanceSmall"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop = "16dp"
android:background = "@color/colorPrimary"
android:text = "@string/action_save"
android:textColor = "@android:color/white"
android:textStyle = "bold" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
|
If there is an inflate error because of com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout, add the following line to the gradle file:
implementation 'com.google.android.material:material:1.0.0'
|
The
strings.xml file is given as follows:
|
MyFirebase\app\res\values\strings.xml
|
<resources>
<string name="app_name">My Firebase</string>
<string name="hint_name">Full Name</string>
<string name="hint_email">Email</string>
<string name="action_save">Save</string>
<string name="name">Name</string>
<string name="email">Email</string>
</resources>
|
The
dimens.xml file is given as follows:
|
MyFirebase\app\res\values\dimens.xml
|
<resources>
<!-- Default screen margins, per the Android Design guidelines. -->
<dimen name="activity_horizontal_margin">16dp</dimen>
<dimen name="activity_vertical_margin">16dp</dimen>
</resources>
|
The
styles.xml file is given as follows:
|
MyFirebase\app\res\values\styles.xml
|
<resources>
<!-- Base application theme. -->
<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
<!-- Customize your theme here. -->
<item name="colorPrimary">@color/colorPrimary</item>
<item name="colorPrimaryDark">@color/colorPrimaryDark</item>
<item name="colorAccent">@color/colorAccent</item>
</style>
</resources>
|
The
colors.xml file is given as follows:
|
MyFirebase\app\res\values\colors.xml
|
<resources>
<color name="colorPrimary">#00bcd4</color>
<color name="colorPrimaryDark">#0097a7</color>
<color name="colorAccent">#0097a7</color>
</resources>
|
The
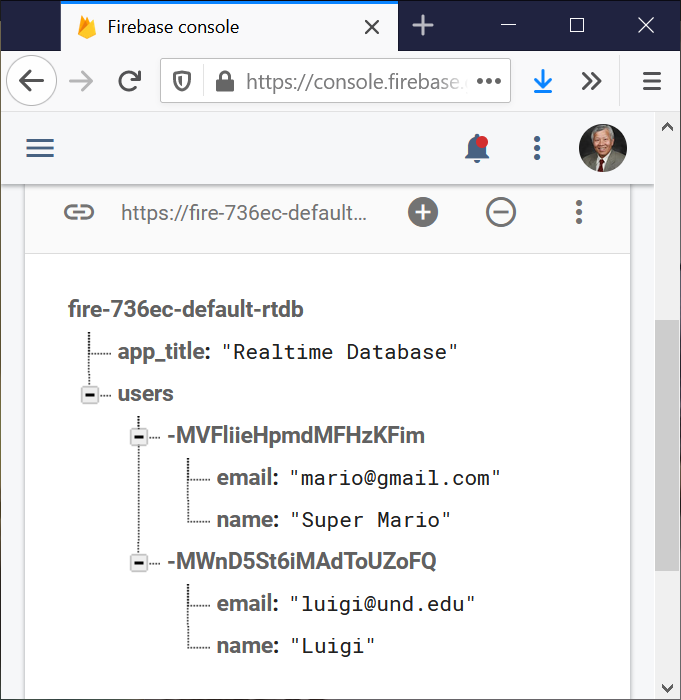
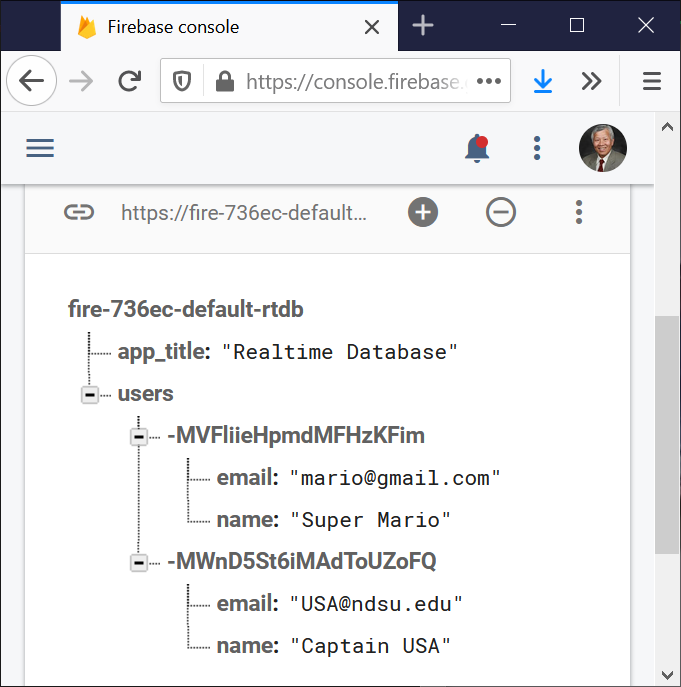
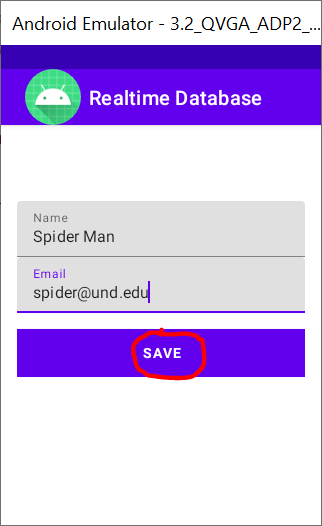
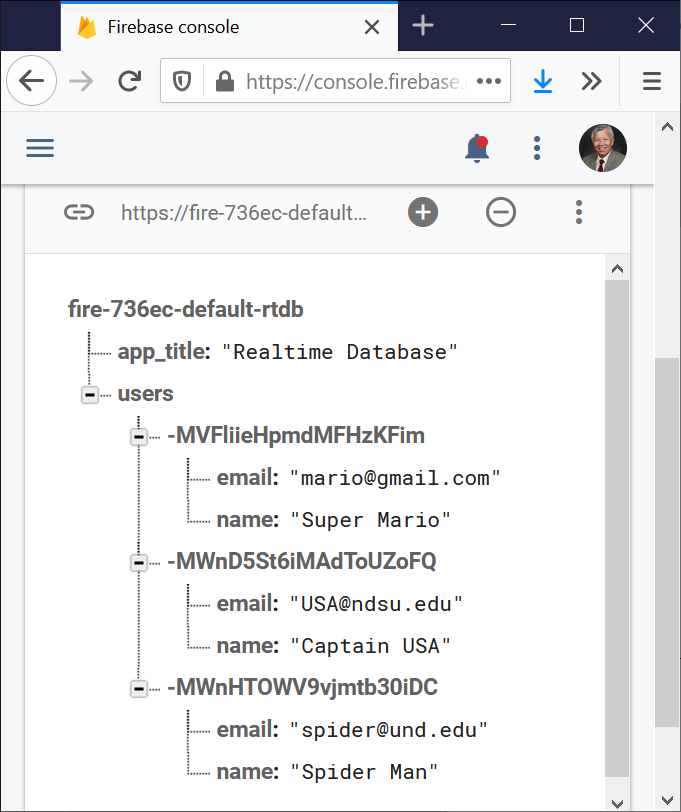
MainActivity.java program saves the name and email address of a user in the Firebase database when starts a new session (emulator).
Afterwards, only the current user’s profile (name and email address) can be updated unless another session starts, and the previous profiles are not able to be updated.
|
MyFirebase\app\java\com\wenchen\myfriebase\MainActivity.java
|
package com.wenchen.myfirebase
import android.os.Bundle;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.google.firebase.database.DataSnapshot;
import com.google.firebase.database.DatabaseError;
import com.google.firebase.database.DatabaseReference;
import com.google.firebase.database.FirebaseDatabase;
import com.google.firebase.database.ValueEventListener;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName( );
private TextView txtDetails;
private EditText inputName, inputEmail;
private Button btnSave;
private DatabaseReference mFirebaseDatabase;
private FirebaseDatabase mFirebaseInstance;
private String userId;
@Override
protected void onCreate( Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
super.onCreate( savedInstanceState );
setContentView( R.layout.activity_main );
// Displaying toolbar icon
getSupportActionBar( ).setDisplayShowHomeEnabled( true );
getSupportActionBar( ).setIcon( R.mipmap.ic_launcher );
txtDetails = (TextView) findViewById( R.id.txt_user );
inputName = (EditText) findViewById( R.id.name );
inputEmail = (EditText) findViewById( R.id.email );
btnSave = (Button) findViewById( R.id.btn_save );
mFirebaseInstance = FirebaseDatabase.getInstance( );
// Getting reference to 'users' node
mFirebaseDatabase = mFirebaseInstance.getReference( "users" );
// Storing app title to 'app_title' node
mFirebaseInstance.getReference( "app_title" ).setValue( "Realtime Database" );
// app_title change listener
mFirebaseInstance.getReference( "app_title" ).addValueEventListener(
new ValueEventListener( ) {
@Override
public void onDataChange( DataSnapshot dataSnapshot ) {
Log.e( TAG, "App title updated" );
String appTitle = dataSnapshot.getValue( String.class );
// Updating toolbar title
getSupportActionBar( ).setTitle( appTitle );
}
@Override
public void onCancelled( DatabaseError error ) {
// Failed to read value
Log.e( TAG, "Failed to read app title value.", error.toException( ) );
}
}
);
// Saving or updating the user
btnSave.setOnClickListener(
new View.OnClickListener( ) {
@Override
public void onClick( View view ) {
String name = inputName.getText( ).toString( );
String email = inputEmail.getText( ).toString( );
// Checking for already existed userId
if ( TextUtils.isEmpty( userId ) ) createUser( name, email );
else updateUser( name, email );
}
}
);
toggleButton( );
}
// Changing button text
private void toggleButton( ) {
if ( TextUtils.isEmpty( userId ) ) btnSave.setText( "Save" );
else btnSave.setText( "Update" );
}
//
// Creating new user node under 'users'
//
private void createUser( String name, String email ) {
// TODO
// In real apps this userId should be fetched by using auth
if ( TextUtils.isEmpty( userId ) )
userId = mFirebaseDatabase.push( ).getKey( );
User user = new User( name, email );
mFirebaseDatabase.child( userId ).setValue( user );
addUserChangeListener( );
}
//
// User data change listener
//
private void addUserChangeListener( ) {
mFirebaseDatabase.child( userId ).addValueEventListener(
new ValueEventListener( ) {
@Override
public void onDataChange( DataSnapshot dataSnapshot ) {
User user = dataSnapshot.getValue( User.class );
// Check for null
if ( user == null ) {
Log.e( TAG, "User data is null!" );
return;
}
Log.e( TAG, "User data is changed!" + user.name + ", " + user.email );
// Displaying newly updated name and email
txtDetails.setText( user.name + ", " + user.email );
// Clearing edit text
inputEmail.setText( "" );
inputName.setText ( "" );
toggleButton( );
}
@Override
public void onCancelled( DatabaseError error ) {
// Failed to read value
Log.e( TAG, "Failed to read user", error.toException( ) );
}
}
);
}
private void updateUser( String name, String email ) {
// Updating the user via child nodes
if ( !TextUtils.isEmpty( name ) )
mFirebaseDatabase.child( userId ).child( "name" ).setValue( name );
if ( !TextUtils.isEmpty( email ) )
mFirebaseDatabase.child( userId ).child( "email" ).setValue( email );
}
}
|
In order to save a user profile, we use a model class called
User.java file to store the properties of name and email address (you can add few more properties like address, phone number, etc.):
|
MyFirebase\app\java\com\wenchen\myfriebase\User.java
|
package com.wenchen.myfirebase
import com.google.firebase.database.IgnoreExtraProperties;
@IgnoreExtraProperties
public class User {
public String name;
public String email;
// Default constructor required for calls to
// DataSnapshot.getValue( User.class )
public User( ) { }
public User( String name, String email ) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
}
}
|
Start testing the project:
|

|
⇒ |

|
⇒ |
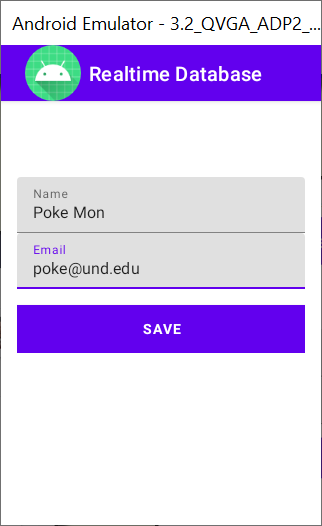
|
| |
⇒ |
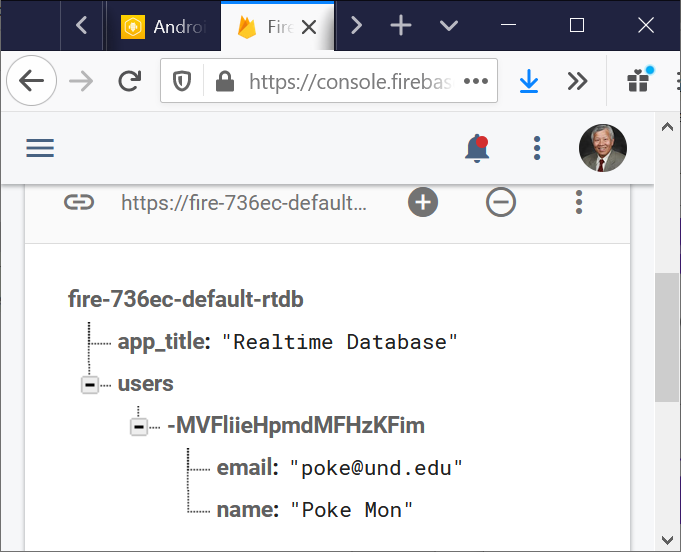
|
⇒ |

|
⇒ |

|
| |
New
session |
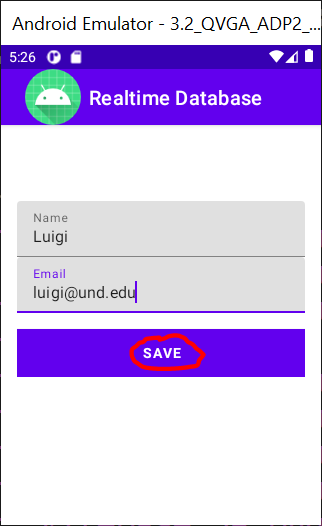
|
⇒ |
|
⇒ |

|
| |
⇒ |
|
| |
New
session |
|
⇒ |
|
⇒ |

|