|
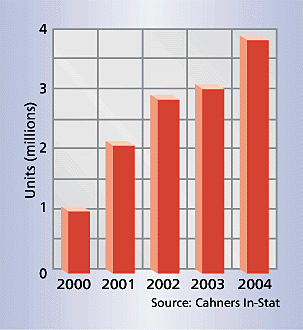
LAN Standard The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard is rapidly gaining popularity. As the figure shows, sales will increase to 3.9 million by 2004. The technology's security mechanism is the WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) protocol. |
|
|
LAN Standard The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard is rapidly gaining popularity. As the figure shows, sales will increase to 3.9 million by 2004. The technology's security mechanism is the WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) protocol. |

|