Wireless Networks (Cont.)
Wireless networking technologies are advancing at a tremendous pace and each represents a solution for a certain phase, such as 1G, 2G, and 3G, in a particular geographical area, such as the US, Europe, or Japan. The figure shows the mobile network migration, in which the GSM technology path will become the most widely accepted standard for 3G services.
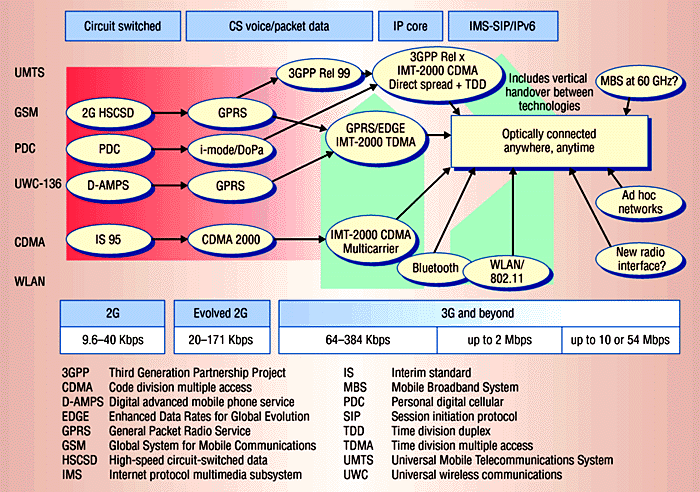
The generally accepted 3G migration path is to upgrade the GSM network to the 2.5G GPRS.
With a data transfer rate of up to 171 kilobits per second, more than 10 times current standards, GPRS provides more effective mobile data capabilities.
The GSM/GPRS network will in turn evolve into EDGE and finally into the UMTS, with speeds in excess of 2 megabits per second. Each standard is based on and provides an upgrade path for at least one of today's primary wireless interfaces: TDMA, GSM, and CDMA.

