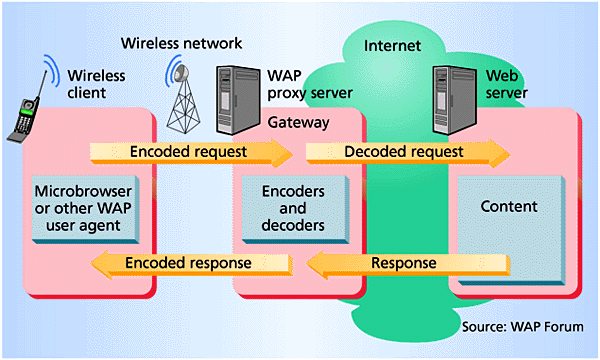
Slide 16.10: Mobile middleware
Slide 16.12: WAP demonstrations
Home

|
Slide 16.10: Mobile middleware Slide 16.12: WAP demonstrations Home |

|
| WAP | i-mode | |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | Open Mobile Alliance | NTT DoCoMo |
| Function | A protocol | A complete mobile Internet service |
| Host Language | WML (Wireless Markup Language) | cHTML (compact HTML) |
| Major Technology | WAP Gateway | Packet switched |
| Security | WTLS (Wireless Transport Layer Security) | SSL (Secure Socket Layer) |
| Key Features | Widely adopted and flexible | Highest number of users and easy to use |