|
||||||||
| Database | JDBC | Oracle | PL/SQL | SQL | SQL Developer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SQL*Plus | Oracle OR 12c | Object-oriented Oracle | SQL Cheat 1 | SQL Cheat 2 | ||||
| Software/Tool | Java | Perl | Unix shell | Emacs | Linux | |||
| Web Tool | CGI | (X)HTML | W3Schools | CGI 101 | ||||
| General Information | Discord | EE/CS Wiki | EITS | UND help | Stackoverflow | |||
| Syllabus: Fall 2025 | Credit hours: 3 | |||
| Class times: 9:30am – 10:45am, TuTh | Classroom: Witmer Hall 209 | |||
| Class # (on-campus: 520-01): 19267 | Class # (on-line: 520-02): 19268 | |||
| Instructor: Wen-Chen Hu (my teaching philosophy) | Office: Upson II 366K | |||
 Email: wenchen@cs.und.edu Email: wenchen@cs.und.edu
|
||||
| Office hours: 2:30pm – 4:30pm, MoWeFr | ||||
Prerequisites:
|
||||
| Synchronous class delivery:
The class lectures will be delivered synchronously via |
||||
| Lecture notes: No textbook will be used. Instead award-winning, interactive, informative, and practical lecture notes (based on books, papers, online documents, and user manuals) and detailed and precise class instructions will be provided. Collectively, the lecture notes and instructions are more like a small book, which supplies much more information than regular notes do and makes the subject studies much easier. Students will not have problem learning the subjects or taking the exams after studying them and doing programming exercises. | ||||
Grading: |
|
Announcements:
- Updated constantly: Class notes
- Tuesday, December 16: Final Exam to be held at 6:30pm–8:30pm (CST) for everyone
- Wednesday, December 10: Final Exam Question Distribution posted
- Tuesday, November 18: Exam II to be held at 6:30pm–8:30pm (CST) for everyone
- Thursday, November 06: Exam II Question Distribution posted
- Thursday, December 04: Programming Exercise II due
- Thursday, October 02: Programming Exercise II posted
- Tuesday, October 07: Exam I to be held at 6:30pm–8:30pm (CST) for everyone
- Monday, September 29: Exam I Question Distribution posted
- Thursday, October 02 (soft): Programming Exercise I due
- Tuesday, August 26: Programming Exercise I posted
- Tuesday, August 26: Check a simple CGI test page at
A CGI Test Page
If you follow it very carefully, you should be able to make the CGI scripts work. - Tuesday, August 26: To extend the connection time of SQL Developer, use the following method:
You could turn DBMS output (like collection types) on and setting the polling frequency (refresh) to once every 2 minutes or so by selecting the following SQL Developer options:⇒ ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ ⇒ 120 - Tuesday, August 26:
Execute the following command at the server
undcemcs02for the first time and only time. Otherwise, your CGI scripts will not work.
shell⯈ chcon -R -t httpd_sys_script_exec_t /home/USER.ID/public_html
Swap out “USER.ID” with your login name:
shell⯈ chcon -R -t httpd_sys_script_exec_t /home/first.lastname/public_html
- Tuesday, August 26: Edit your
.bash_profilefile at the serverundcemcs02.und.eduby using the following command (you can use any other editor, not just emacs) for the first and only time:
shell⯈ emacs ~/.bash_profile
where the~/.bash_profilefile can be found from here and is the personal initialization file, executed for login shells. - Monday, August 25: Register this course via Course Registration.
Tentative Schedule:
Week |
Class | Topic | Due | Where | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0. Computer Career and Data Research & Technologies | |||||||
| 0.1 A computer career | ||||||||
| 0.2 Data research | ||||||||
| 0.3 Data technologies | ||||||||
| 1 | 08/26 08/28 |
1. Introduction to DATA 520 | ||||||
| 1.1 Course outline | ||||||||
| 1.2 Tentative schedule | ||||||||
| 1.3 Software to be used | ||||||||
| 2 | 09/02 09/04 |
2. Programming Exercise I | ||||||
| 2.1 Specifications | ||||||||
| 2.2 A sample website | ||||||||
| 2.3 Construction steps | ||||||||
| 09/03 |
Last day to add a course or drop without record — 100% refund Last day to add audit or change to/from audit Last day to receive a refund on a dropped class Drops after the last day to add will appear on a transcript. |
|||||||
| 3 | 09/09 09/11 |
3. Essential Technologies for Exercise Construction | ||||||
| 3.1 HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) | ||||||||
| 3.2 CGI (Common Gateway Interface) | ||||||||
| 3.3 Using Oracle | ||||||||
| 4 | 09/16 09/18 |
4. Internet-Enabled Database Construction | ||||||
| 4.1 Technologies for website building | ||||||||
| 4.2 Website construction summary | ||||||||
| 4.3 An example | ||||||||
| 5 | 09/23 09/25 |
5. Database Models | ||||||
| 5.1 Relational databases | ||||||||
| 5.2 Object-oriented databases | ||||||||
| 5.3 Database market share | ||||||||
| 6 | 09/30 10/02 |
6. Oracle Databases | ||||||
| 6.1 Oracle Database 21c | ||||||||
| 6.2 Oracle SQL*Plus | ||||||||
| 6.3 Oracle data dictionary | ||||||||
| 7 | 10/09 | 7. Web-JDBC Programming | ||||||
| 7.1 Programming Exercise II | ||||||||
| 7.2 Associating an ID with a web page | ||||||||
| 7.3 Building HTML pages dynamically | ||||||||
| 10/07 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 8 | 10/14 10/16 |
8. JDBC Programming | ||||||
| 8.1 Database connection | ||||||||
| 8.2 Query execution | ||||||||
| 8.3 Prepared SQL | ||||||||
| 9 | 10/21 10/23 |
9. JDBC Programming (Cont.) | ||||||
| 9.1 Processing the result set | ||||||||
| 9.2 A dynamic database access | ||||||||
| 9.3 Committing changes | ||||||||
| 10 | 10/30 | 10. Relational Model | ||||||
| 10.1 Introduction | ||||||||
| 10.2 Relational tables | ||||||||
| 10.3 Relational rules | ||||||||
| 10/28 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 11 | 11/04 11/06 |
11. Relational Algebra | ||||||
| 11.1 Introduction | ||||||||
| 11.2 Set theoretic operations | ||||||||
| 11.3 Native relational operations | ||||||||
| 12 | 11/13 | 12. SQL Query Language | ||||||
| 12.1 SQL commands | ||||||||
| 12.2 SQL Data Definition Language (DDL) | ||||||||
| 12.3 SQL Data Manipulation Language (DML) | ||||||||
| 11/14 |
Last day to change to or from S/U grading Last day to change to or from audit grading Last day to drop a full-term course or withdraw from school |
|||||||
| 11/11 |
|
|||||||
| 13 | 11/20 | 13. Database Design | ||||||
| 13.1 Basic modeling concepts | ||||||||
| 13.2 Entity-relationship (E-R) model | ||||||||
| 13.3 Transformation rules | ||||||||
| 11/18 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 14 | 11/25 | 14. SQL Query Language (Cont.) | ||||||
| 14.1 Advanced data manipulation commands | ||||||||
| 14.2 SQL examples | ||||||||
| 14.3 Power of SQL | ||||||||
| 11/26 11/27 11/28 |
|
|||||||
| 15 | 12/02 12/04 |
15. Database Design (Cont.) | ||||||
| 15.1 Database normalization | ||||||||
| 15.2 Normal forms |  |
|||||||
| 15.3 Normalization examples | ||||||||
| 12/02 |
|
|||||||
| 16 | 12/09 12/11 |
16. |
||||||
| 16.1 Normalization | ||||||||
| 16.2 Normal forms | ||||||||
| 16.3 A case study | ||||||||
| 17 | 12/16 |
|
||||||
| 18 | 12/23 | Grades posted before noon, Tuesday |
According to Google, Top-10 popular computer careers (05/18/2025) are listed as follows:
However, without a proven track record, a computer/data-science graduate may face one of the highest unemployment rates (6.1%) because companies want employees to start contributing immediately according to Newsweek (05/24/2025). Computer/data science is different from many other disciplines (like electrical engineering). It is more like a professional school (such as culinary schools), which emphasizes practical works instead of subject studies. There are three kinds of computing personnel:
Remark I: Definitions, terminologies, and theories will be discussed minimally in this course. Instead practical works and programming knowledge will be emphasized and enforced. The old technology, CGI (Common Gateway Interface), will be used to connect the Web to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) programs because of the limited resources provided by the CEM, but CGI has no problem implementing the features used by other technologies (like ASP.NET or PHP). Also, the focus of this course is on databases, instead of Web-database connection.
Remark II: Database technologies like programming languages have no breakthroughs for years, so old, new, these, or those textbooks are pretty much the same. In other words, not much database research is left to do. However, databases are still a useful tool for other research areas like data science including data (web) mining and discovery, information retrieval, and mobile data management (e.g., location-based services). Don’t mention databases are a must tool for many applications such as e/m-commerce sites and IT systems.
Remark III: Web, mobile, and database programming is a must for IT developers, and the only effective way to learn software development is practicing, instead of studying concepts or writing some testing programs.
Remark IV:
According to a study, students in computer courses learn much more by building large-scale exercises instead of many small-scale test programs, which give fragmented knowledge contrary to solid understanding of the system.
Remark V: Remote work is a trend for IT workers. This course also allows you to learn how to do it by using the VPN (virtual private networks) to connect to our Linux server
Instructor’s qualification: The instructor’s PhD dissertation is titled “An image database system based on a linear skeleton representation,” which includes a database-driven web system by using Perl and Sybase in 1997, when not many people were familiar with the Web. In fact, all his research to date uses or relates to databases, but not tries to build or enhance a DBMS (database management system). In addition, he is familiar with many kinds of databases like Oracle, MySQL, Google Firebase, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server & Access, Sybase, and MongoDB.
University of North Dakota Course Descriptions (DATA 520) —
An introduction to the principles of database design and management. Topics include query optimization, procedural extension of query languages, runtime error handling, normalization techniques, data warehousing, and NoSQL.
Database Outline —
A collection of information organized in such a way that a computer program can quickly select desired pieces of data. To access information in a database, you need a database management system (DBMS), which is a collection of programs that enables you to enter, organize, and select data in a database.
An Internet-Enabled and Mobile Database Course Sequence —
This is part of an Internet/mobile-enabled database course sequence offered by me:
The following platforms, software, and tools used in these courses greatly help students land a decent job:
|

|
However, without a proven track record, a computer/data-science graduate may face one of the highest unemployment rates (6.1%) because companies want employees to start contributing immediately according to Newsweek (05/24/2025). Computer/data science is different from many other disciplines (like electrical engineering). It is more like a professional school (such as culinary schools), which emphasizes practical works instead of subject studies. There are three kinds of computing personnel:
- Developers:
- Positions (plenty): Developers of front-end and back-end web pages, mobile apps, and all kinds of software
- Skills (more stable): Programming languages (such as C++ and Java), web programming, mobile app development, data processing and management including databases, and data structures & algorithms
- Practitioners:
- Positions (not many): Experienced personnel like data scientists, database or system administrators, security analysts, and network architects (more applications & configuration and less development)
- Skills (based on the needs of companies): Databases, data warehousing, data lake, Hadoop, MapReduce, Linux, SPSS, SAS, Cogno, Matlab, Tableau, etc.
- Researchers:
- Industrial positions (few and based on the needs of corporations): High quality personnel required for the advanced areas like artificial intelligence, security, computer vision, autonomous driving, and speech recognition
- Academic positions/trends (few and changed according to the government policies): ❓ ⇐ artificial intelligence ⇐ big data ⇐ high-performance computing ⇐ security ⇐ (mobile) networks
Remark I: Definitions, terminologies, and theories will be discussed minimally in this course. Instead practical works and programming knowledge will be emphasized and enforced. The old technology, CGI (Common Gateway Interface), will be used to connect the Web to JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) programs because of the limited resources provided by the CEM, but CGI has no problem implementing the features used by other technologies (like ASP.NET or PHP). Also, the focus of this course is on databases, instead of Web-database connection.
Remark II: Database technologies like programming languages have no breakthroughs for years, so old, new, these, or those textbooks are pretty much the same. In other words, not much database research is left to do. However, databases are still a useful tool for other research areas like data science including data (web) mining and discovery, information retrieval, and mobile data management (e.g., location-based services). Don’t mention databases are a must tool for many applications such as e/m-commerce sites and IT systems.
Remark III: Web, mobile, and database programming is a must for IT developers, and the only effective way to learn software development is practicing, instead of studying concepts or writing some testing programs.
No pain, no gain 😂
Remark V: Remote work is a trend for IT workers. This course also allows you to learn how to do it by using the VPN (virtual private networks) to connect to our Linux server
undcemcs02.und.edu, and having the exercises set up at the server and be accessed from the clients.
Instructor’s qualification: The instructor’s PhD dissertation is titled “An image database system based on a linear skeleton representation,” which includes a database-driven web system by using Perl and Sybase in 1997, when not many people were familiar with the Web. In fact, all his research to date uses or relates to databases, but not tries to build or enhance a DBMS (database management system). In addition, he is familiar with many kinds of databases like Oracle, MySQL, Google Firebase, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server & Access, Sybase, and MongoDB.
University of North Dakota Course Descriptions (DATA 520) —
An introduction to the principles of database design and management. Topics include query optimization, procedural extension of query languages, runtime error handling, normalization techniques, data warehousing, and NoSQL.
Database Outline —
A collection of information organized in such a way that a computer program can quickly select desired pieces of data. To access information in a database, you need a database management system (DBMS), which is a collection of programs that enables you to enter, organize, and select data in a database.
|
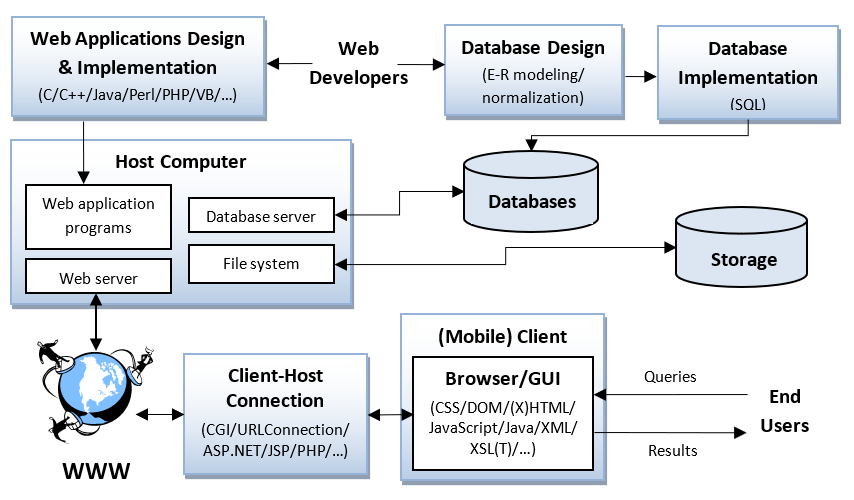
A System Structure of a Generic Internet/Mobile-Enabled Database System — |
|
An Internet-Enabled and Mobile Database Course Sequence —
This is part of an Internet/mobile-enabled database course sequence offered by me:
CSCI 399 .NET and World Wide Web Programming
⇓
CSCI 457 Electronic and Mobile Commerce Systems
⇓
DATA 520 Databases
⇓
CSCI 513 Advanced Database Systems
⇓
CSCI 515 Data Engineering and Management
⇓
DATA 525 Data Engineering and Mining
- CSCI 399 (.NET and World Wide Web Programming) to build database-driven websites by using
- Microsoft SQL Server database,
- Microsoft ASP.NET,
- Microsoft C#,
- Microsoft .NET, and
- Microsoft Visual Studio.
- CSCI 457 (Electronic and Mobile Commerce Systems) to build electronic and mobile commerce systems by using
- Android programming,
- Android-server-database connection,
- (L) Linux operating system,
- (A) Apache web server,
- (M) MySQL database, and
- (P) PHP.
- DATA 520 (Databases) to build Internet-enabled database systems by using
- Client/web-server-database connection,
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity),
- Oracle database, and
- Relational database design and SQL.
- CSCI 513 (Advanced Database Systems) to build Internet-enabled and embedded database systems by using
- Android programming,
- Android SQLite embedded database,
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity),
- Object-relational SQL and PL/SQL, and
- Oracle (an object-relational database).
- CSCI 515 (Data Engineering and Management) to build location-based services and data-mining systems to discover knowledge from a large set of data by using
- Android programming,
- Android Google APIs and Firebase database,
- Data mining and knowledge discovery,
- Information retrieval,
- Location-based services, and
- Smartphones and mobile handheld devices.
- DATA 525 (Data Engineering and Mining) to build Internet-enabled data-mining systems to discover knowledge from a large set of data by using
- Data mining and knowledge discovery,
- Internet-enabled Firebase database,
- Information retrieval, and
- Internet-enabled TensorFlow.