The
SELECT statement is used to select data from a database.
| The result is stored in a result table (called the result-set). The syntax on the right is for the select statement: |
|
An SQL Select Example
Assume the table
person is given as follows:
| person_id | last_name | first_name | address | city |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hansen | Ola | Timoteivn 10 | Sandnes |
| 2 | Svendson | Tove | Borgvn 23 | Sandnes |
| 3 | Pettersen | Kari | Storgt 20 | Stavanger |
To select the columns named
last_name and first_name, use a select statement like this:
SELECT last_name, first_name FROM person; LAST_NAME FIRST_NAME --------------------------- --------------------------- Hansen Ola Svendson Tove Pettersen Kari |
Now we want to select all the columns from the
person table.
We use the following select statement:
SELECT * FROM person; PERSON_ID LAST_NAME FIRST_NAME ADDRESS CITY --------- ------------- -------------- ------------- ----------- 1 Hansen Ola Timoteivn 10 Sandnes 2 Svendson Tove Borgvn 23 Sandnes 3 Pettersen Kari Storgt 20 Stavanger |
Demonstration
Below is an SQL test area from W3Schools, which uses the well-known Northwind sample database. The tables here are for read only because of the problem of embedding the scripts. For a fully working example, check this by using Chrome.
|
Result:
|
The Database includes:
|
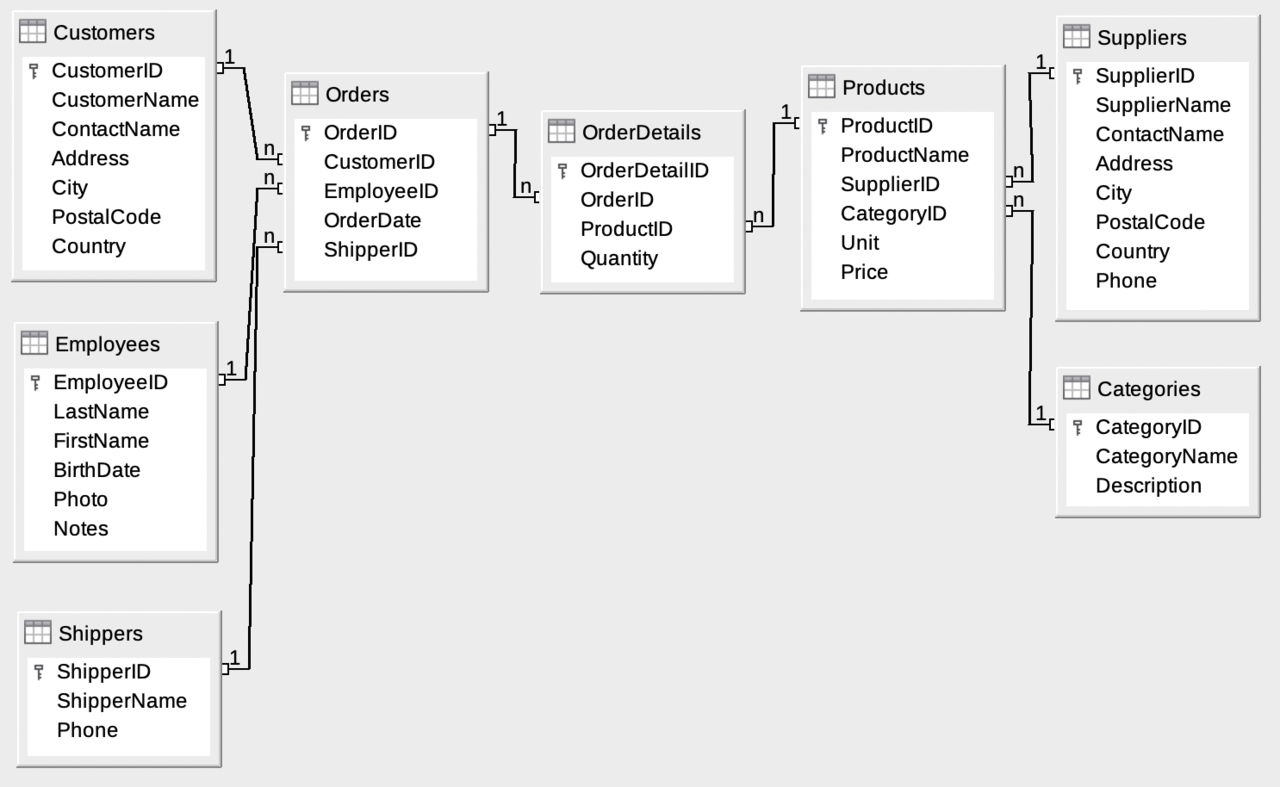
|
The Database includes:
|