To model the behavior of a random web surfer, Google forms the matrix:
G = αS + (1 - α)Iv, where
0≤α<1-
The damping factor, α, in the Google matrix indicates that random web surfers move to a different webpage by some means other than selecting a link with probability
1-α. I, a column vector of ones-
For example,
I=(1 1 1 1)T. v, a row probability distribution vector-
The majority of experiments performed during the development of the PageRank algorithm used
α=0.85andv=(1/n 1/n ...1/n). Assigning the uniform vector forvsuggests web surfers randomly choose new webpages to view when not selecting links.
Since each element Gij of G lies between 0 and 1 (0≤Gij≤1) and the sum of elements in each row of G is 1.
The following gives an example of G calculation for the web graph on the right.
|
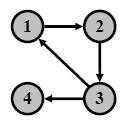
|
G = αS + (1 - α)Iv
0.00 1.00 0.00 0.00 1
= 0.85×[ 0.00 0.00 1.00 0.00 ] + (1-0.85)×[ 1 ]×[ 0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 ]
0.50 0.00 0.00 0.50 1
0.25 0.25 0.25 0.25 1
0.0000 0.8500 0.0000 0.0000 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375
= [ 0.0000 0.0000 0.8500 0.0000 ] + [ 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375 ]
0.4250 0.0000 0.0000 0.4250 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375
0.2125 0.2125 0.2125 0.2125 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375 0.0375
0.0375 0.8875 0.0375 0.0375 3/80 71/80 3/80 3/80
= [ 0.0375 0.0375 0.8875 0.0375 ] = [ 3/80 3/80 71/80 3/80 ]
0.4625 0.0375 0.0375 0.4625 37/80 3/80 3/80 37/80
0.2500 0.2500 0.2500 0.2500 1/4 1/4 1/4 1/4
|
Once in a blue moon (very rarely) you see the Aurora here, but it is not like farther north. |