File processing refers to the use of computer files to store data in persistent memory (i.e. the data is stored even after the computer has been turned off and restarted). It has several advantages and disadvantages over database systems, for example, it requires the user to define and implement files for each application. This can be done either permanently in the computer code of the program, or by user selection when the program is running.
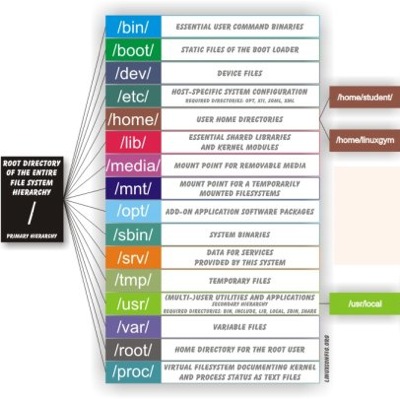
| Like other operating systems, Unix organizes user data, programs, etc. into structures called files. Files, in turn, are placed in directories. Directories are organized into a hierarchical structure, something like an upside down tree. This entire structure, including all of the directories and files, as well as the special structures the operating system uses to keep track of them, is called a file system. |
|