Types
Each class is assigned a type which defines the attributes applicable to the objects.
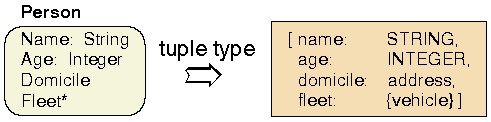
Substitutability
An object should be substitutable by objects of its subclasses. Thus, the type of the subclass must be a subtype of the type of the superclass in an appropriate sense. A type
T’ is a subtype of the type T and vice versa T is a supertype of T’, if either T = T’ or the following conditions apply:
- If
Tis a class, then every subclassT’ofTis a subtype ofT. - If
Tis a tuple type, thenT’is a subtype ofT, ifT’is also of tuple type and every attribute inTis defined forT’as well. Moreover, for corresponding attributes theT’-type must be a subtype of theT-type. - If
Tis a set type, thenT’is a subtype ofT, ifT’is also a set type and the element type ofT’is a subtype of the element type ofT.
SELECT a FROM a IN employee WHERE a.domicile.location = a.driver.domicile.location; |
Late Binding
Substitutability of objects and redefinition of methods requires late binding.
Determine all employees whose successindicator > 50.
|
|
|
I’ve just invented a great new iPhone alarm app. If you press the snooze button 3 times it automatically emails your boss telling them that your gonna be sick. |