You can create a user-defined datatype and then use the new datatype in a relational table. The data actually resides as column values in the table, rather than the column value being a pointer (
REF) to the data.
| This methodology creates a column object or nested object that |
|
- Does not have an object identifier.
- Cannot be referenced using the
REFoperator.
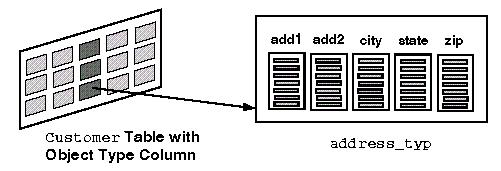
The
address_typ type is used as the datatype for the cust_address column of a customer relational table.
When object types are instantiated in this way, you create a column object or nested object.
If the user-defined type is in another schema, you must use the schema name as a qualifier of the datatype.
For example, if user scott owns scotts_typ object, use:
CREATE TABLE my_table( x scott.scotts_typ );

