The files strings.xml and dimens.xml are not required, but they make programming much easier.
For example, assuming the name appears 10 times in your program, you have to modify the name 10 times if the name is changed.
However, if you use the strings.xml, you only have to change the name once and it will be applied to the whole project.
The following string variables are used in this app:
|
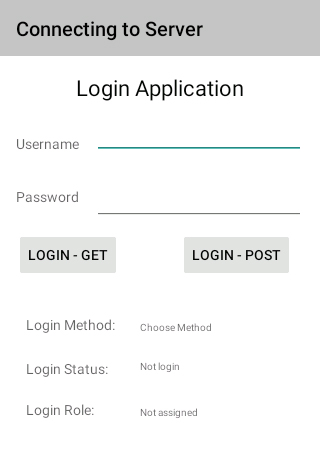
|
|
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="app_name">Server Connection</string> <string name="home_page">Connecting to Server</string> <string name="Name">Username</string> <string name="Pword">Password</string> <string name="LoginGet">Login - Get</string> <string name="LoginPost">Login - Post</string> <string name="App">Login Application</string> <string name="LoginStatus">Login Status:</string> <string name="LoginRole">Login Role:</string> <string name="Status">Not login</string> <string name="Role">Not assigned</string> <string name="method">Login Method:</string> <string name="Choose">Choose Method</string> </resources> |
The
dimens.xml is as follows:
|
|
<resources> <!-- Default screen margins, per the Android Design guidelines. --> <dimen name="activity_horizontal_margin">16dp</dimen> <dimen name="activity_vertical_margin">16dp</dimen> </resources> |
|
It is better to remain silent at the risk of being thought a fool, than to talk and remove all doubt of it. ― Maurice Switzer, Mrs. Goose, Her Book |