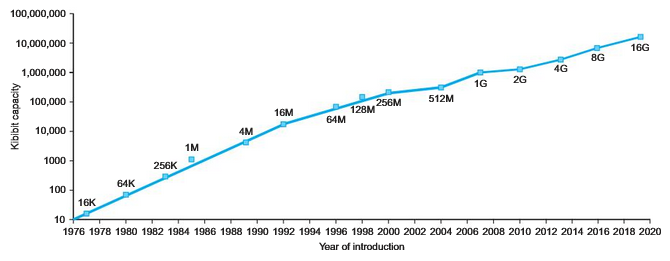
Processors and memory have improved at an incredible rate. The following figure shows the relative performance per unit cost of technologies used in computers over time:
| Year | Technology used in computers | Relative performance/unit cost |
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | Vacuum tube | 1 |
| 1965 | Transistor | 35 |
| 1975 | Integrated circuit (IC) | 900 |
| 1995 | Very large-scale integrated circuit (VLSI) | 2,400,000 |
| 2020 | Ultra large-scale integrated circuit (ULSI) | 500,000,000,000 |
- Vacuum tube is a predecessor of the transistor.
- Transistor is an on/off switch controlled by an electrical signal.
- Integrated circuit (IC) combines dozens to hundred transistors into a single chip.
- Very large-scale integrated circuit (VLSI) contains hundreds of thousands to millions of transistors.