|
Wide Area Network (WAN): The Internet
It extends over hundreds of kilometers that can span a continent. WANs are the backbone of the Internet, which supports the WWW. It is based on optical fibers and is leased from telecommunication companies. |

|
|
Wireless Network: WiFi and Bluetooth
Data is transmitted using radio signals instead of cables. IEEE 802.11 for wireless LAN allows for transmission rates from 1 to nearly 100 million bits/second. |
|
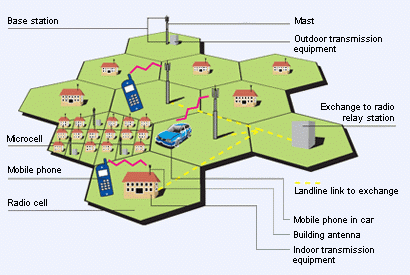
Mobile/Cellular Network: GSM and CDMA
It covers a set of cells/areas. Each cell includes at least one cell tower via which a great number of mobile phones can communicate with each other. |
|
|
“Half of seeming clever is keeping your mouth shut at the right times.” ― Patrick Rothfuss, The Wise Man’s Fear |