A computer cache is a collection of data duplicating original values stored elsewhere or computed earlier, where the original data is expensive to fetch (owing to longer access time) or to compute, compared to the cost of reading the cache.
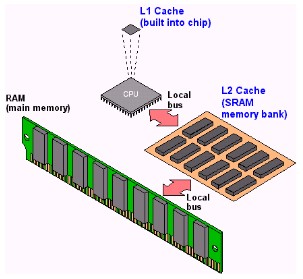
| For example, internal cache (L1) is built into the CPU, and external cache (L2) resides on the motherboard. Both L1 and L2 store data recently used by the CPU. When the CPU needs data, it first checks the fastest source—L1. If the data is not there, the CPU checks the next-fastest source—L2. If the data still cannot be found, a time-consuming search of the slower RAM is required. |
|
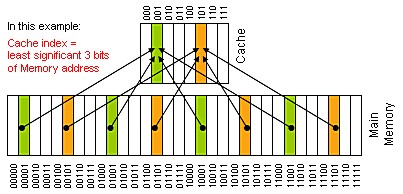
A direct mapped cache is to assign a location in the cache for each word in memory. For example, the following figure shows a direct-mapped cache with eight entries and a memory with 32 words and addresses between 0 and 31. The address
X maps to the direct-mapped cache word with the address X modulo 8”Block address modulo Number of blocks in the cache
|
|
|
“The small wisdom is like water in a glass: clear, transparent, pure. The great wisdom is like the water in the sea: dark, mysterious, impenetrable.” ― Rabindranath Tagore |