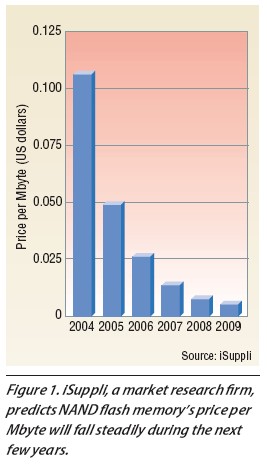
Flash memory's price per Mbyte fell 56 percent from 2004 to 2005, and will fall 47 percent more in 2006 and another 35 percent in 2007. Currently, NAND's storage per Mbyte costs three times as much as minidrives' and 100 times as much as large-capacity drives'.
Capacity
Hard drives generally hold up to 400 Gbytes in PCs and up to 120 Gbytes in laptops. Compact-flash-sized minidrives hold up to 6 Gbytes.