A Generic Structure of a Database-Driven Web System
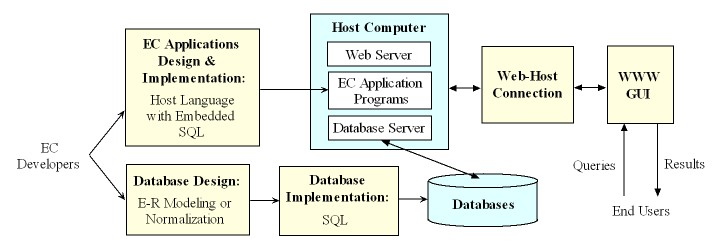
A database-driven web site is often implemented with a three-tiered client-server architecture, which consists of three layers:
- User interface: It runs on a desktop PC or workstation (the client) and uses a standard graphical user interface.
The main function of this tier is to translate tasks and results to something the user can understand.
- Functional module: This tier coordinates the application, processes commands, makes logical decisions and evaluations, and performs calculations.
It also relays data between the two surrounding tiers.
- Database management system (DBMS): A DBMS on a host computer stores and manages the data required by the middle tier for further processing.
The middle tier then sends the processed data back to user.
The three-tier design has many advantages over traditional two-tier or single-tier designs, the chief one being:
The added modularity makes it easier to modify or replace one tier without affecting the other tiers.
†SQL (Structured Query Language), which is a standard interactive language for getting information from and updating a database.
For example, the SELECT statement is used to retrieve data from a database.

