continue Statement
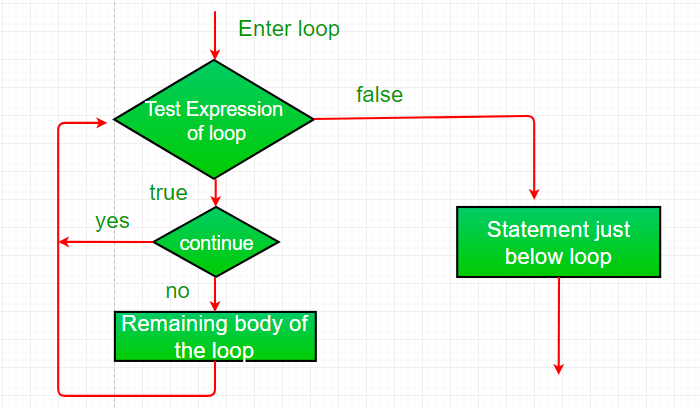
Sometimes it is useful to force an early iteration of a loop. That is to say that you might want to continue running the loop but stop processing the remainder of the code in its body for this particular iteration. The
continue statement breaks one iteration (in the loop), if a specified condition occurs, and continues with the next iteration in the loop.
| This example skips the value of 4: |
|
This is, in effect, a goto just past the body of the loop, to the loop’s end.
The continue statement performs such an action.
|
|
What do you call a dog with no legs? It doesn’t matter, it’s not going to come anyway. |