Arrays
Arrays are used to store multiple values in a single variable.
To declare an array, define the variable type with square brackets.
Either of the following two declarations works.
String[ ] cars;
String vehicles[ ];
|
|
|
|
To insert values to it, we can use an array literal - place the values in a comma-separated list, inside curly braces:
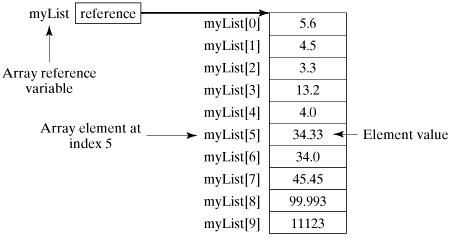
double[ ] myList = new double[10];
String[ ] cars = { "Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda" };
|
|
|
|
Accessing the Elements of an Array
The following statements access the value of the first element in cars, and change the value of a specific element by referring to the index number:
String[ ] cars = { "Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda" };
System.out.println( cars[0] ); // Output: Volvo
cars[0] = "Opel";
System.out.println( cars[0] ); // Now output: Opel instead of Volvo
|
Looping Through an Array
You can loop through the array elements with the
for loop, and use the
length property to specify how many times the loop should run.
The following example outputs all elements in the
cars array:
String[ ] cars = { "Volvo", "BMW", "Ford", "Mazda" };
for ( int i = 0; i < cars.length; i++ ) {
System.out.println( cars[i] );
}
|
|
|
|
|
Living well is the best revenge.
|



