An Example of Runtime Polymorphism
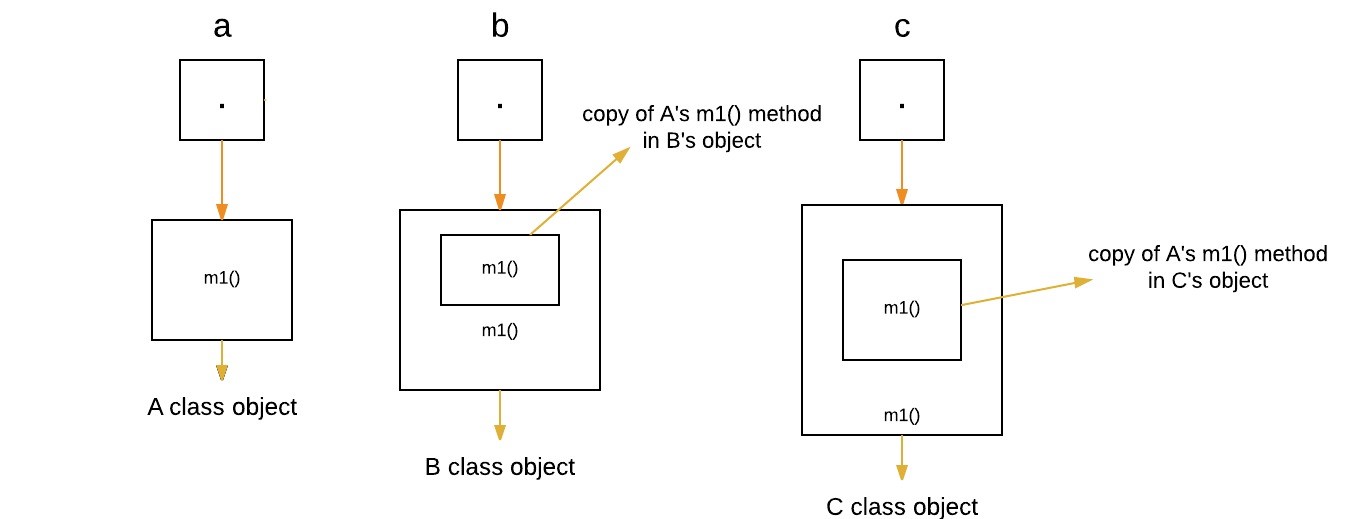
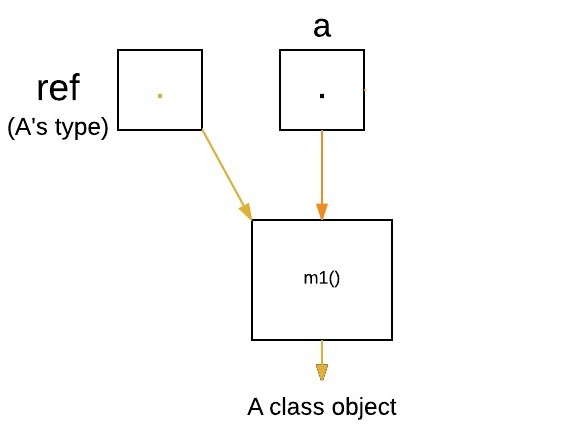
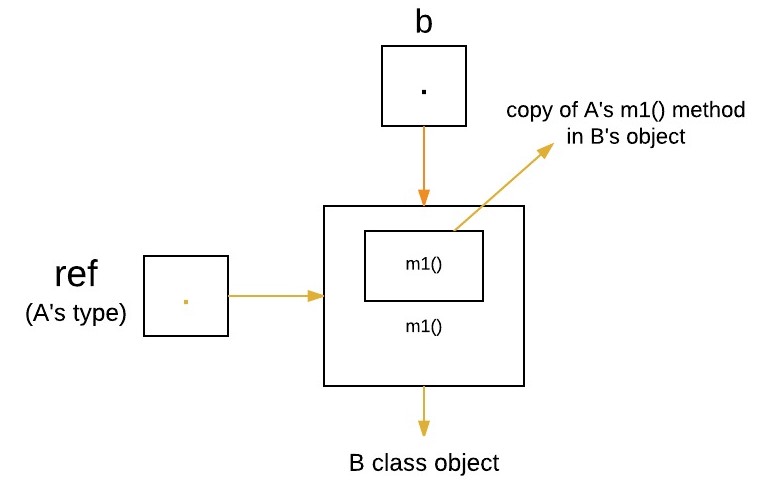
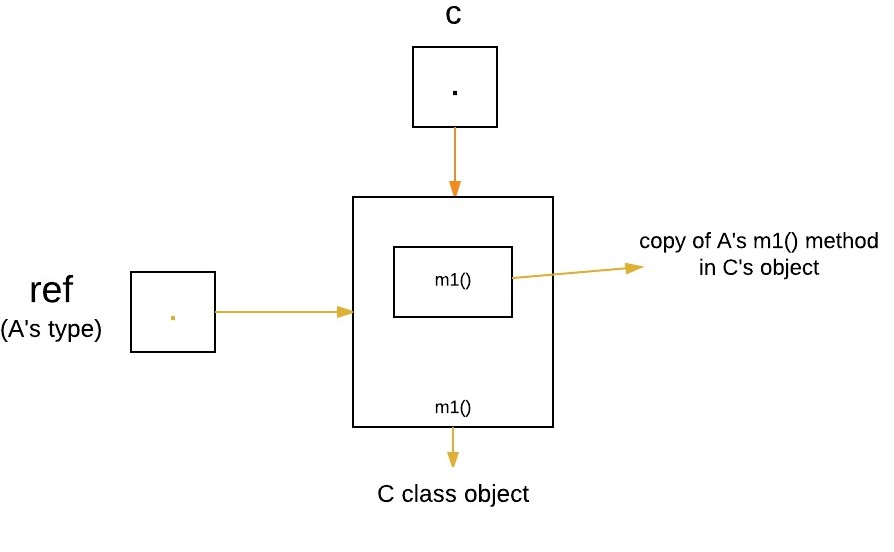
The following program creates one superclass called
A and its two subclasses B and C.
These subclasses override the m1 method.
|
|
|

|
|
|
A and its two subclasses B and C.
These subclasses override the m1 method.
|

|
|

|
|



|