Runtime Polymorphism (or Dynamic Method Dispatch)
Runtime polymorphism is the mechanism by which a call to an overridden method is resolved at run time, rather than compile time.
- When an overridden method is called through a superclass reference, Java determines which version (superclass/subclasses) of that method is to be executed based upon the type of the object being referred to at the time the call occurs. Thus, this determination is made at run time.
- At run-time, it depends on the type of the object being referred to (not the type of the reference variable) that determines which version of an overridden method will be executed.
- A superclass reference variable can refer to a subclass object. This is also known as upcasting. Java uses this fact to resolve calls to overridden methods at run time.
|
|
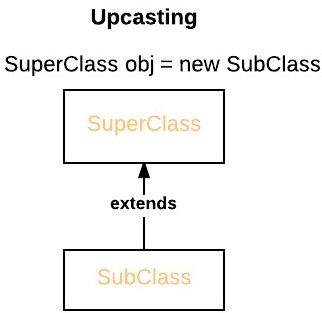
|
Therefore, if a superclass contains a method that is overridden by a subclass, then when different types of objects are referred to through a superclass reference variable, different versions of the method are executed.
Advantages of Runtime Polymorphism
- Dynamic method dispatch allows Java to support overriding of methods which is central for run-time polymorphism.
- It allows a class to specify methods that will be common to all of its derivatives, while allowing subclasses to define the specific implementation of some or all of those methods.
- It also allows subclasses to add their specific methods.