using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApp3 {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
public Form1( ) { InitializeComponent( ); }
private void Compute_Click( object sender, EventArgs e ) {
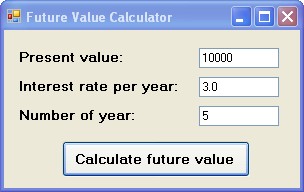
string presentval = PV.Text;
string interest = rate.Text;
string period = years.Text;
double futureVal = FV( presentval, interest, period );
Microsoft.VisualBasic.Interaction.MsgBox(
"The future value is" + futureVal );
}
public double FV( string PV, string i, string n ) {
double result;
result = 1 + double.Parse( i ) / 100;
result = Math.Pow( result, int.Parse( n ) );
result = double.Parse( PV ) * result;
return ( result );
}
}
}
|