|
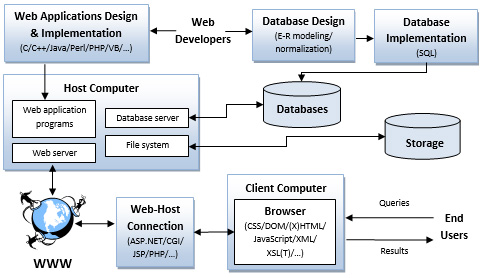
A web-enabled database system is often implemented with a three-tiered client-server architecture, which consists of three layers:
- User Interface
- It runs on a desktop PC or workstation (the client) and uses a standard graphical user interface, which is usually implemented by using (X)HTML and CSS. The main function of this tier is to translate tasks and results to something the user can understand.
- Functional Module
- This level actually processes data. It may consist of one or more separate modules running on a workstation or application server. This tier may be multi-tiered itself. The languages used for this module are usually with embedded SQL such as JDBC and PHP.
- Databases
- A database is an organized collection of structured information, or data, typically stored electronically in a computer system. A database is usually controlled by a database management system (DBMS).

