Matrices/Grids
A matrix represents a collection of numbers arranged in an order of rows and columns. It is necessary to enclose the elements of a matrix in parentheses or brackets.
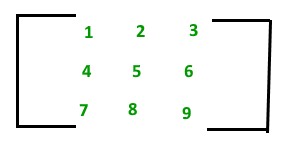
A matrix with 9 elements is shown on the right.
This matrix M has 3 rows and 3 columns.
Each element of matrix M can be referred to by its row and column number; e.g., M[2][3]=6.
|
|
Stacks
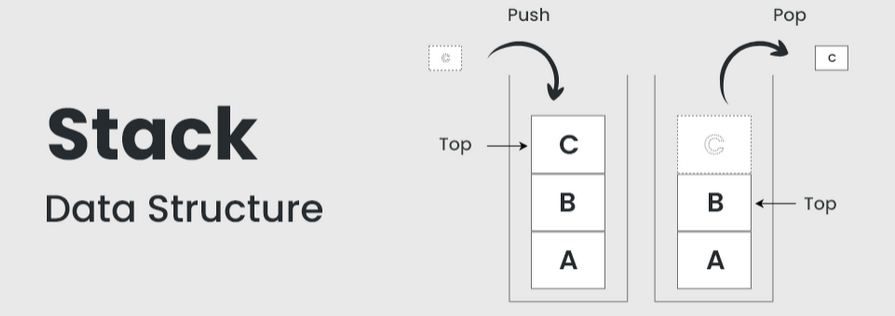
Stack is a linear data structure which follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order may be LIFO (Last In First Out) or FILO (First In Last Out). Stack is considered a complex data structure because it uses other data structures for implementation.
| The other data structures may be arrays, linked lists, etc. based on the characteristics and features of stack data structure. |
|
Queues
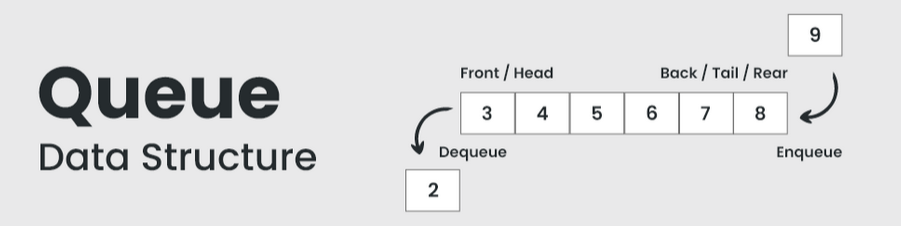
A queue is a linear structure which follows First In First Out (FIFO) approach in its individual operations. A queue can be of different types like
- Circular queue, where the last element is connected to the first element of the queue,
- Double-ended queue (or known as deque), which is a special type of queue where one can perform the operations from both ends of the queue, and
- Priority queue, which is a special type of queue where the elements are arranged as per their priority.
| A low priority element is dequeued after a high priority element. |
|