Databases
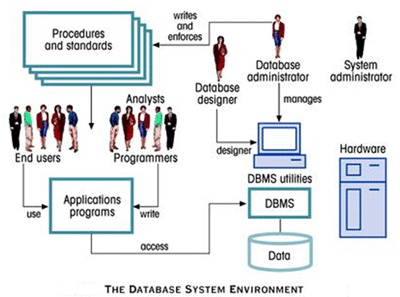
A database is a collection of information organized in such a way that a computer program can quickly select desired pieces of data. In a relational database the data and relations between them are organized in tables.
| A table is a collection of records and each record in a table contains the same fields. To access information from a database, you need a database management system (DBMS). This is a collection of programs that enables you to enter, organize, and select data in a database. |
|
SQL (Structured Query Language)
SQL is a specialized programming language designed for managing and manipulating data stored in databases.
- SQL can execute queries against a database.
- SQL can retrieve data from a database.
- SQL can insert records in a database.
- SQL can update records in a database.
- SQL can delete records from a database.
- SQL can create new databases.
- SQL can create new tables in a database.
Demonstration
Below is an SQL test area from W3Schools, which uses the well-known Northwind sample database. The tables here are for read only because of the problem of embedding the scripts. For a fully working example, check this by using Chrome.
|
Result:
|
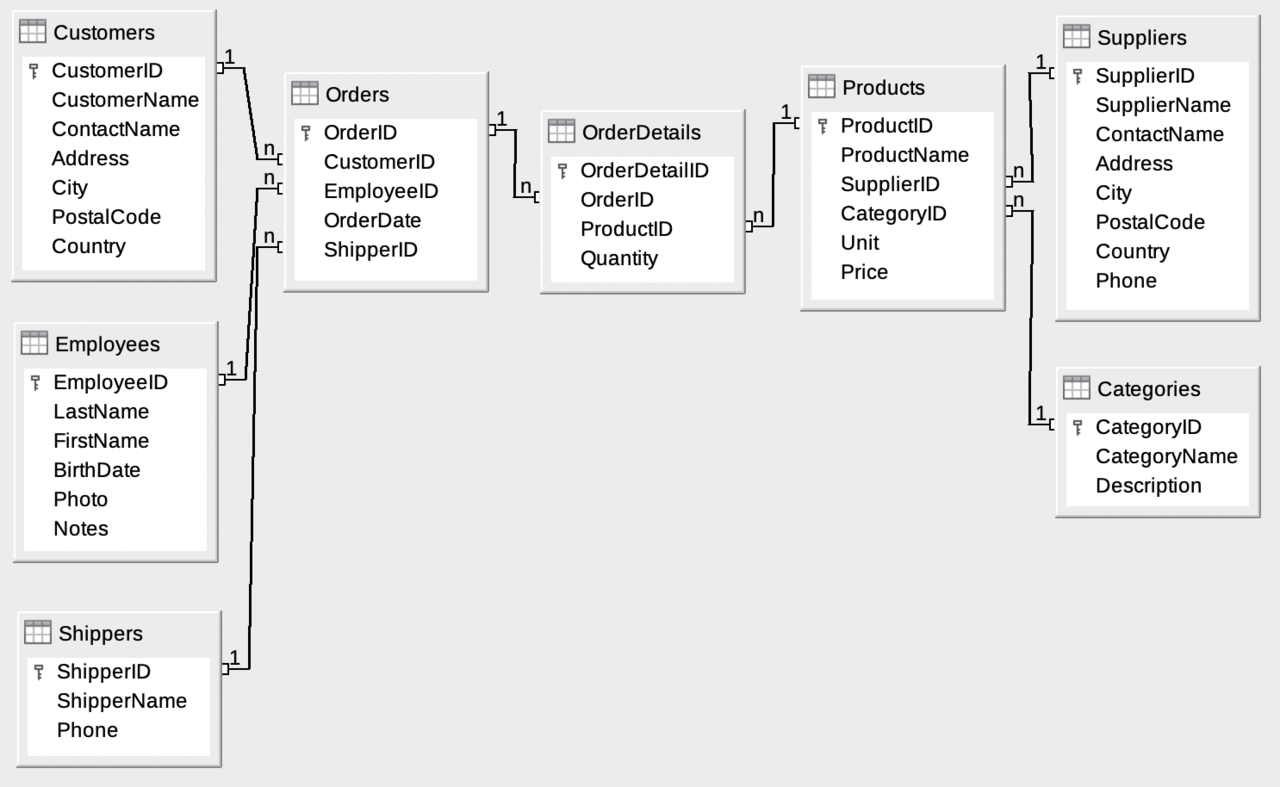
The Database includes:
|
|
The Database includes:
|